60 illustrations including 5 cartoons for 'Structures and Functions of the Kidneys' revision guide in keeping with the Oaka Books style. This was a great opportunity for me as an illustrator to revisit vector work.
Hover over each to read the accompanying captions.
Structures & Functions of the Kidney's, 2019
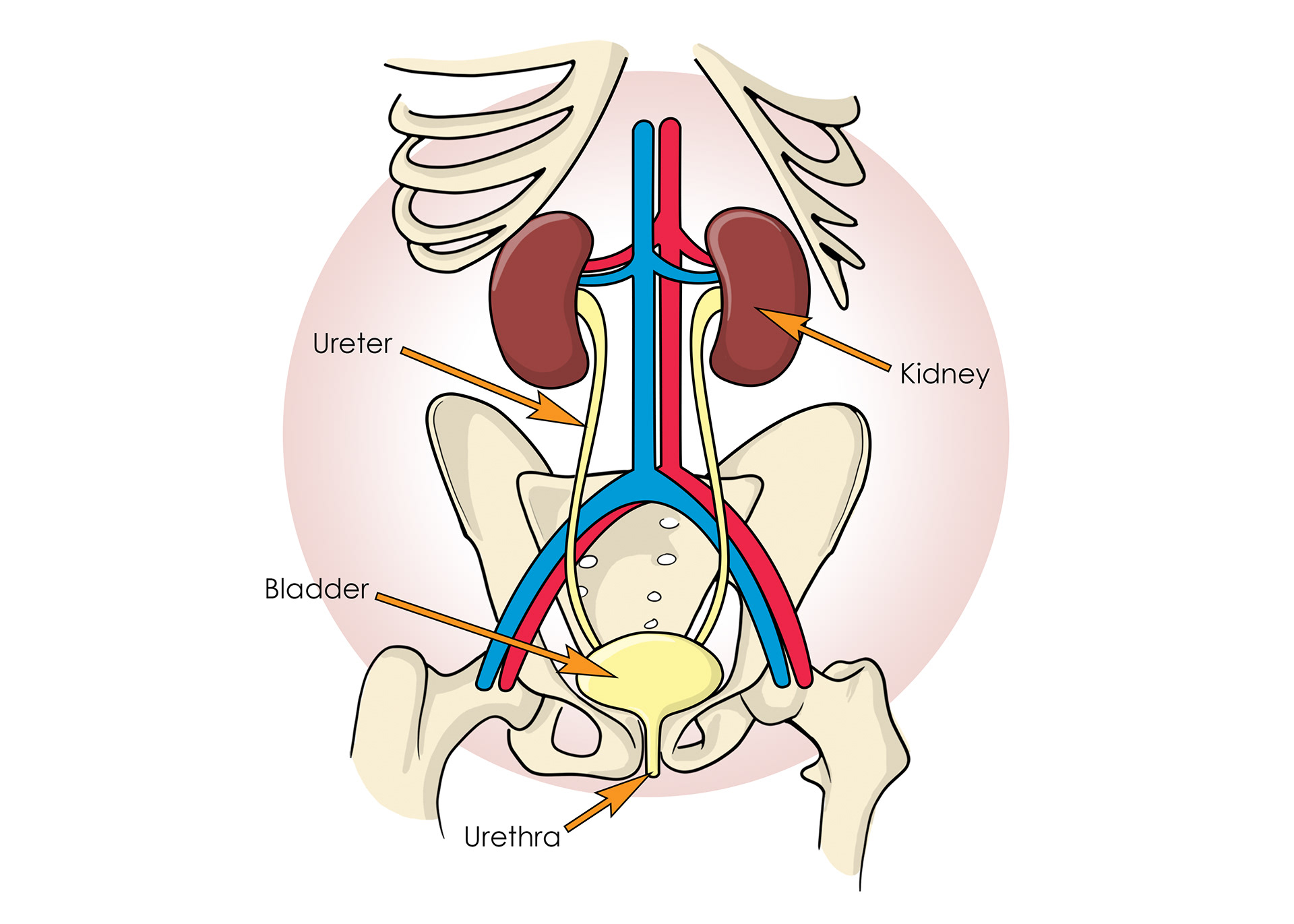
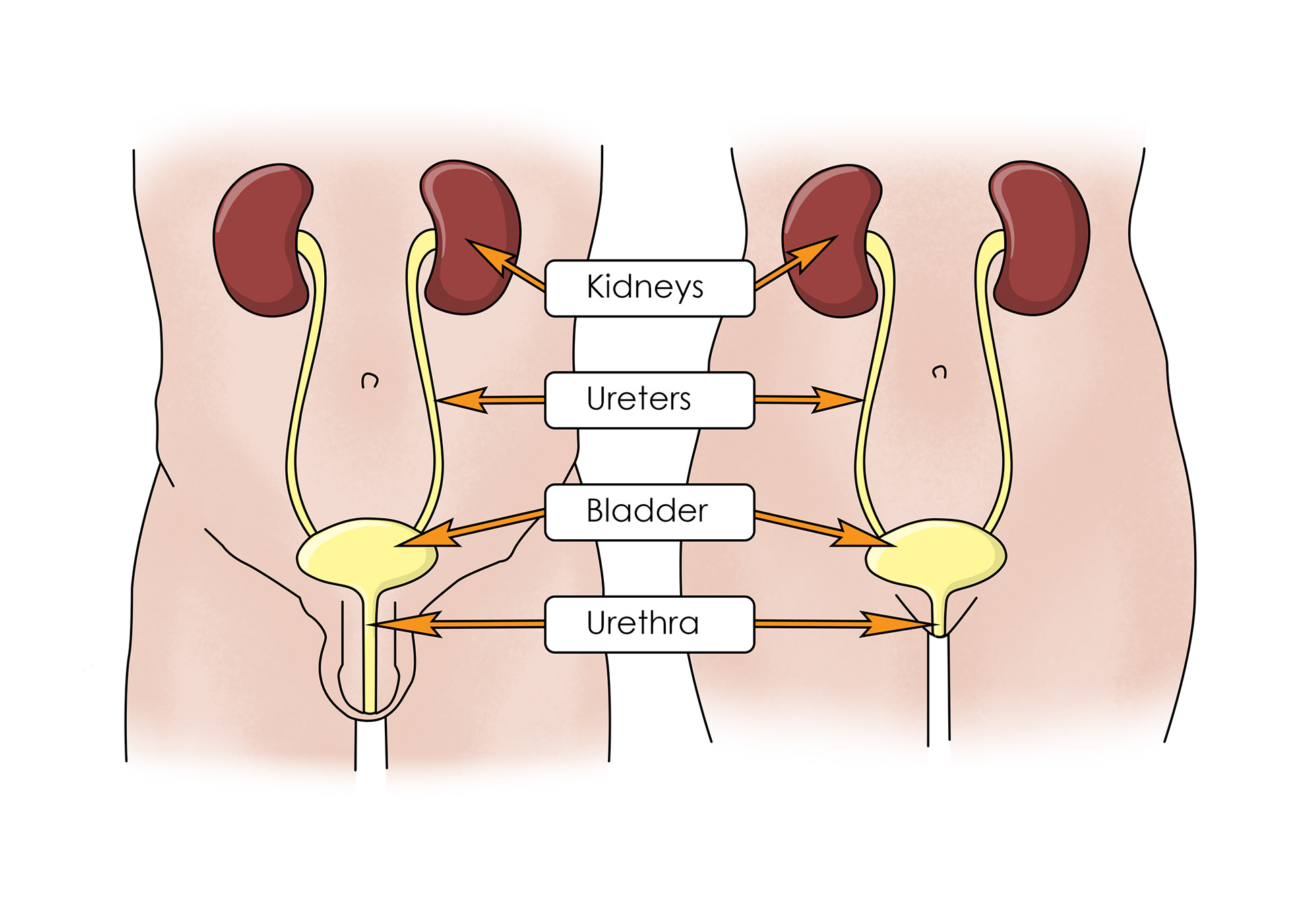
The urinary system
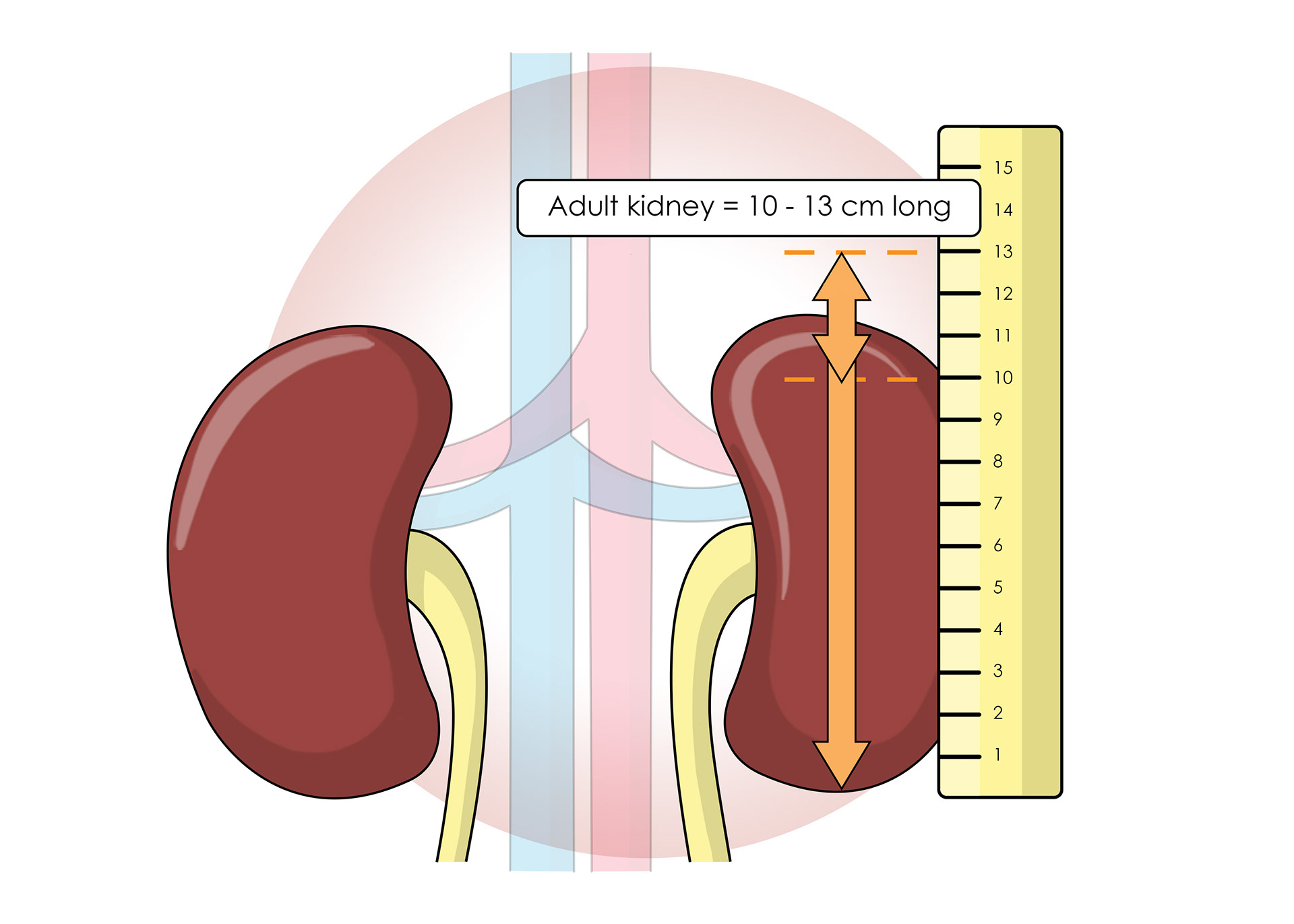
Size of an adult kidney

The kidneys remove toxic waste such as urea from the blood
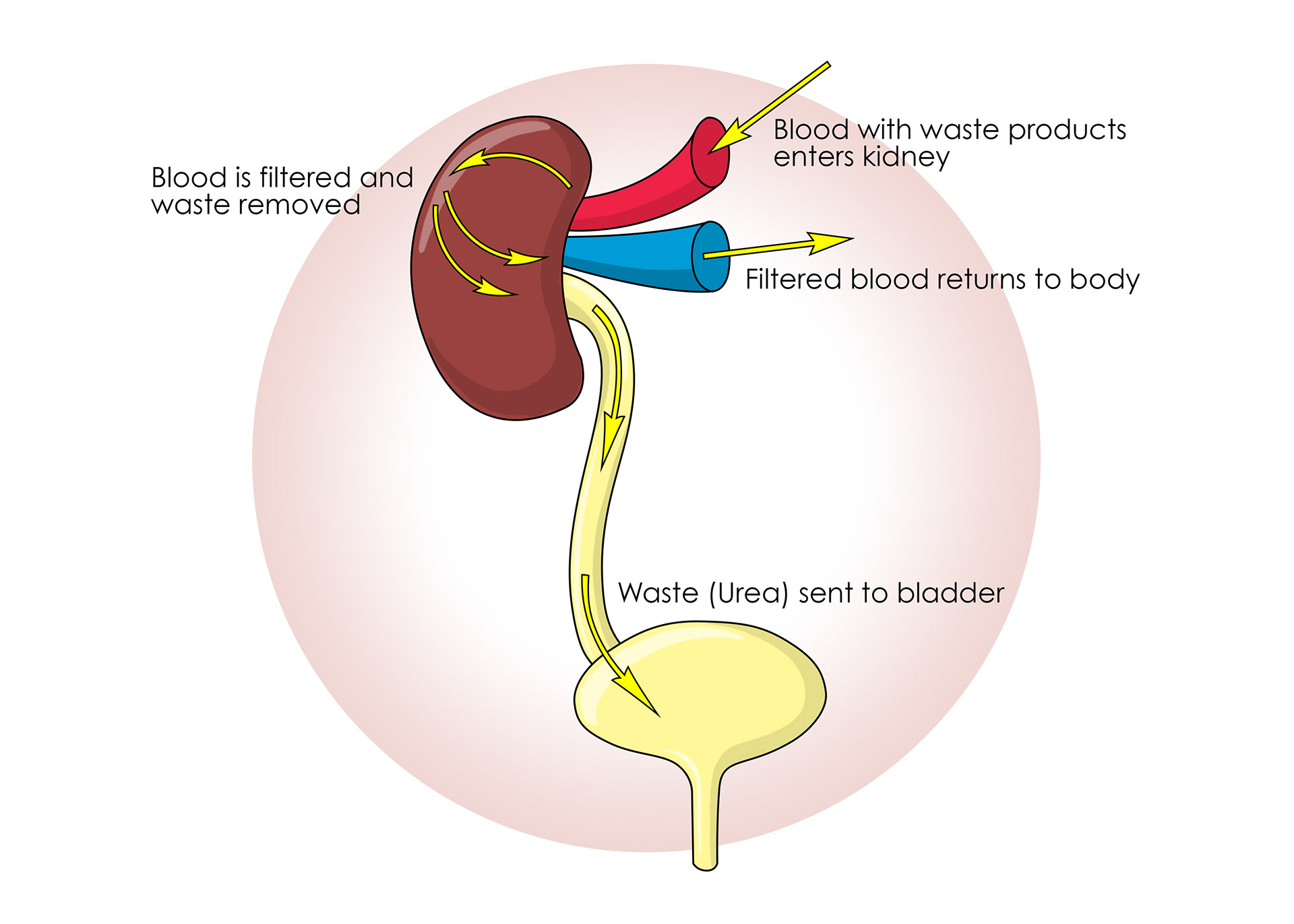
Urea & excess water & salts filtered out
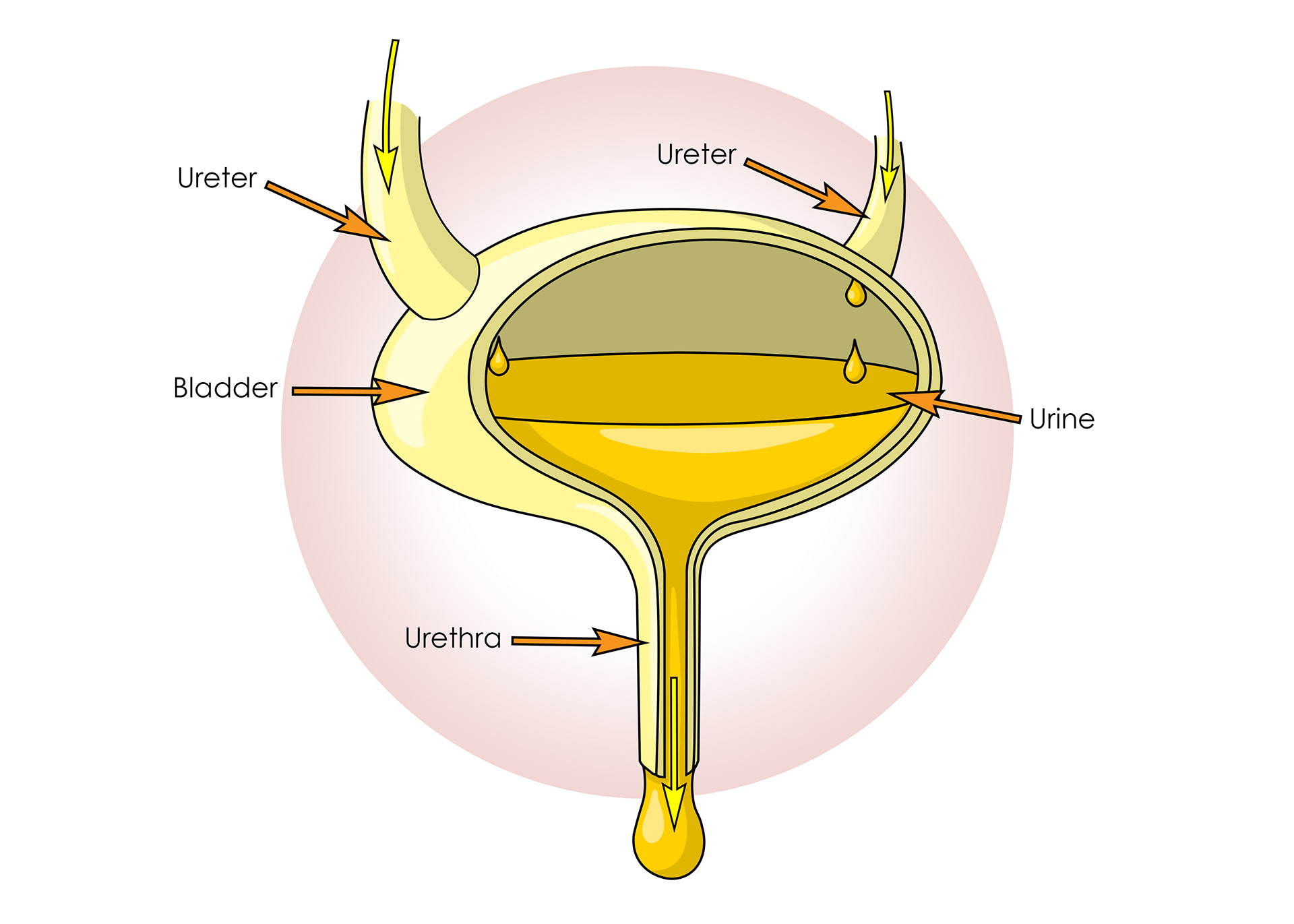
The bladder
Passing urine - the urethra
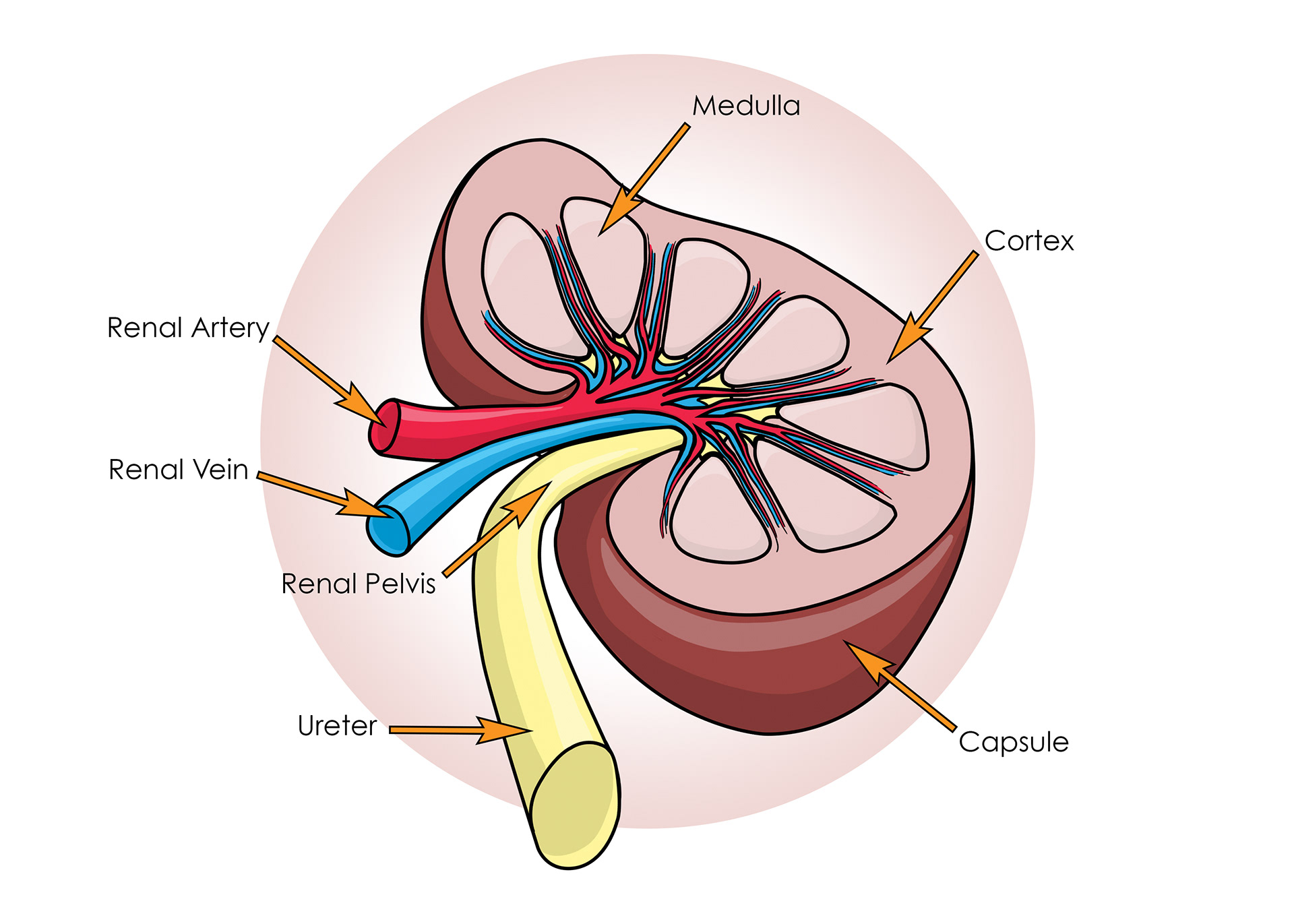
Kidney layers
Nephrons
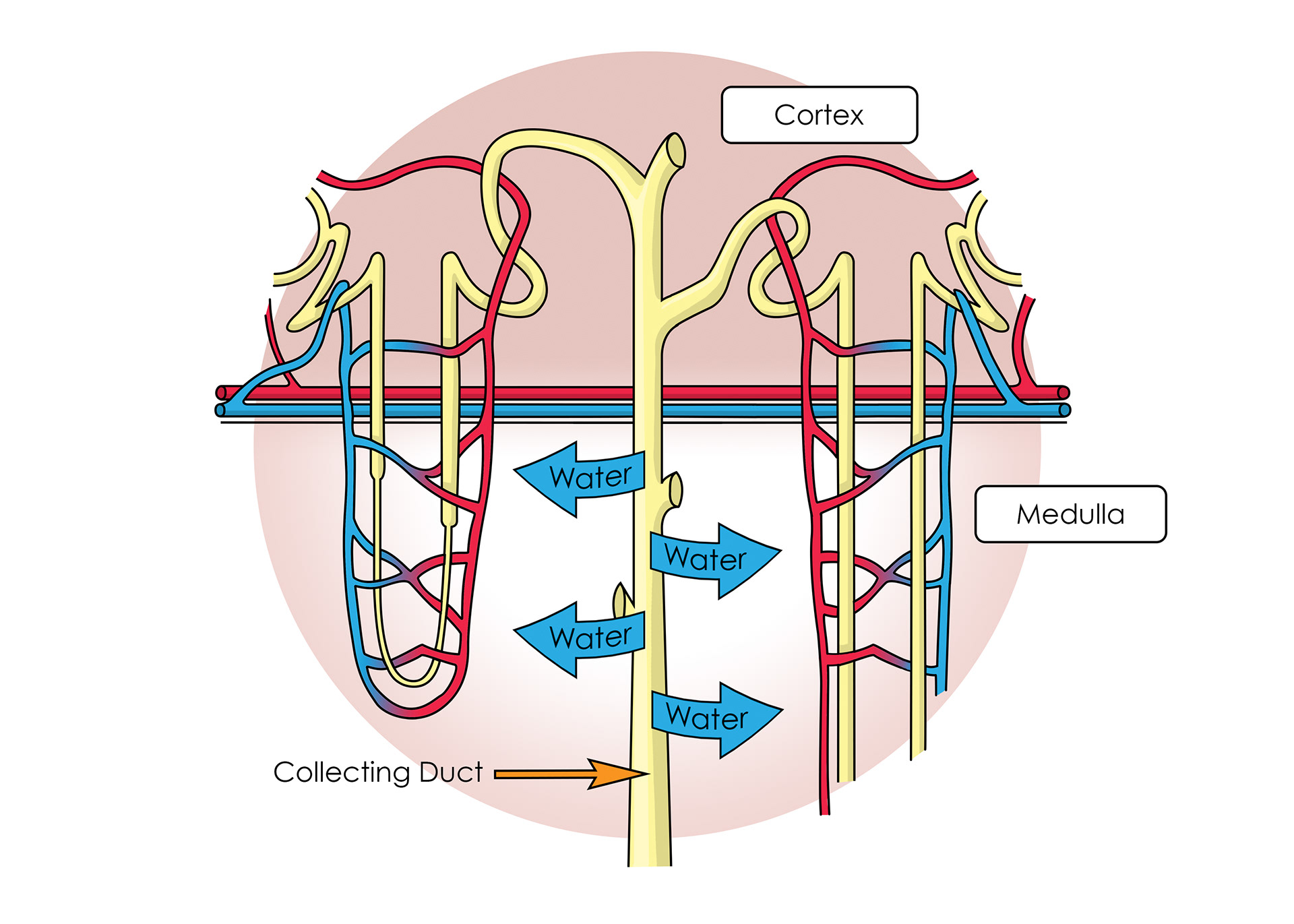
Collecting ducts - where the body reabsorbs water
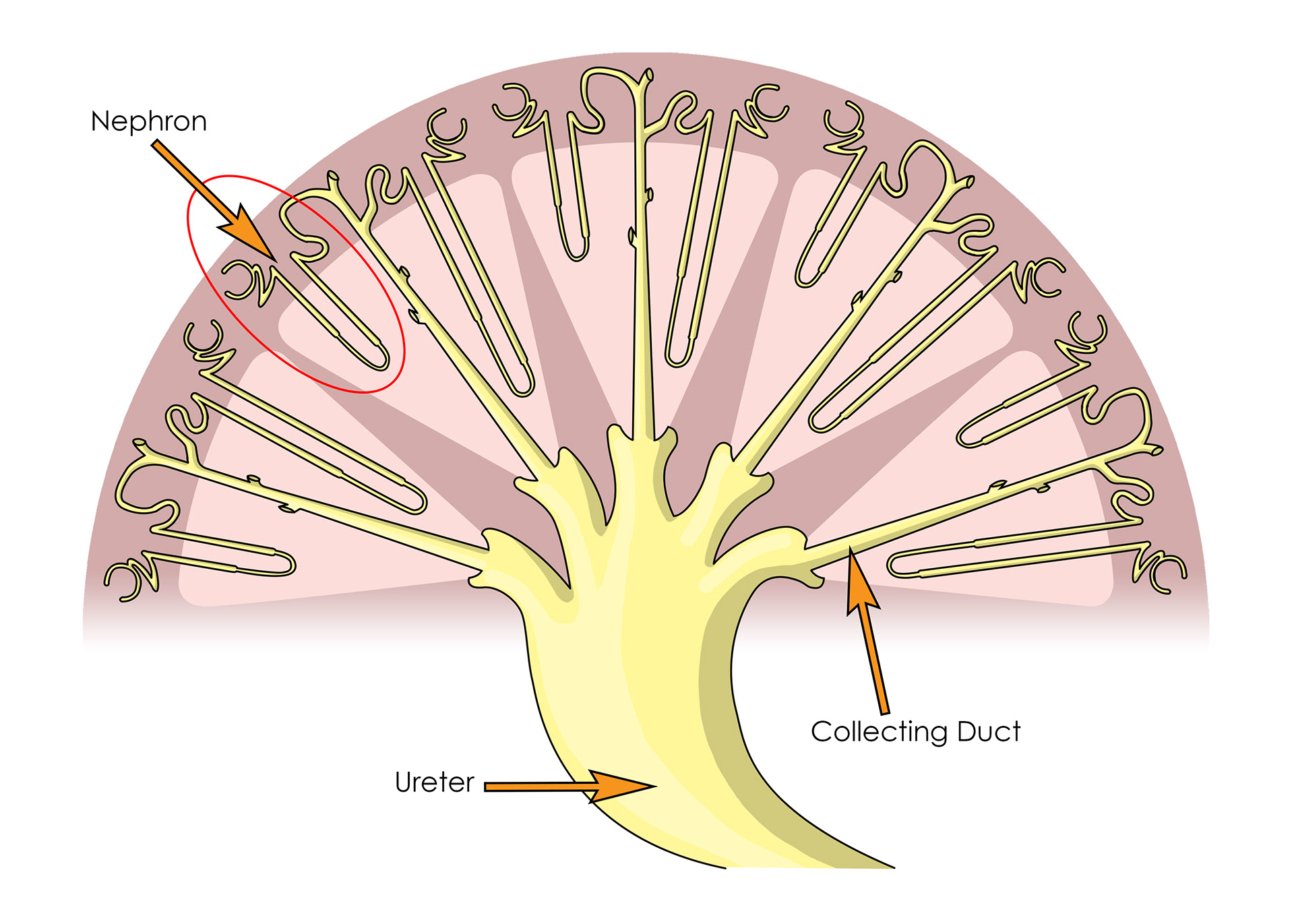
The ureter - branches into collecting ducts & then nephrons
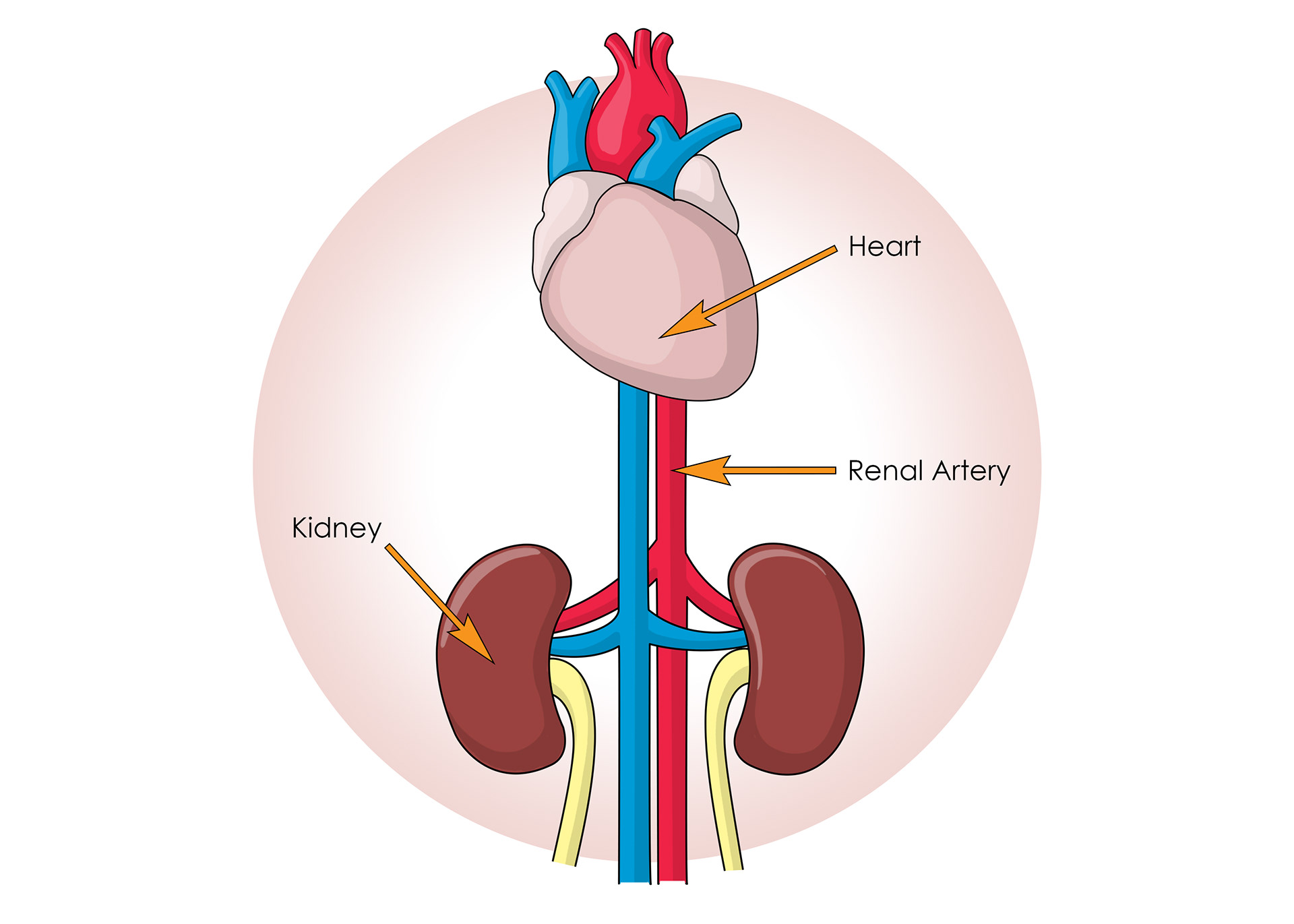
Blood supply from the renal artery
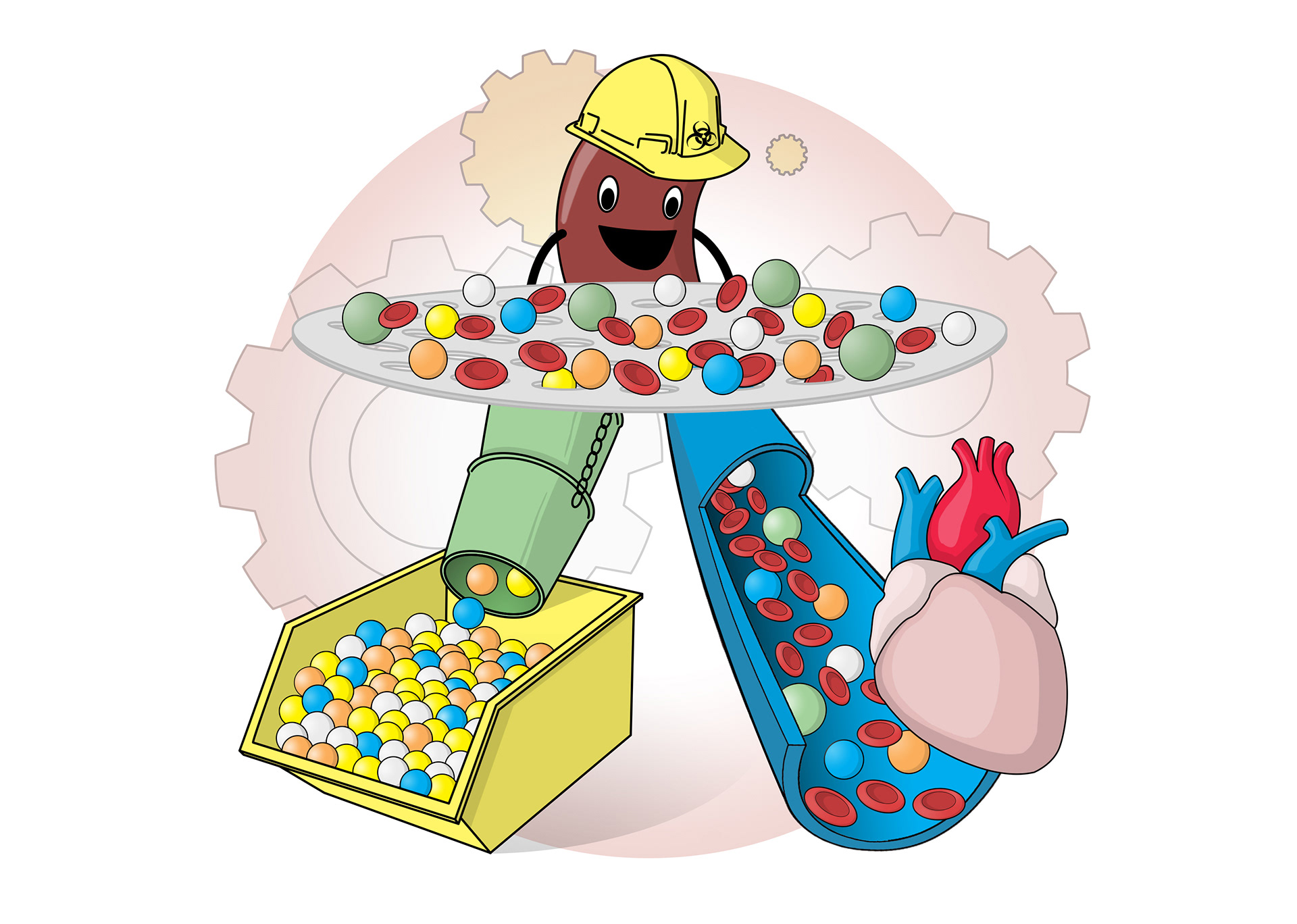
The kidneys clean blood
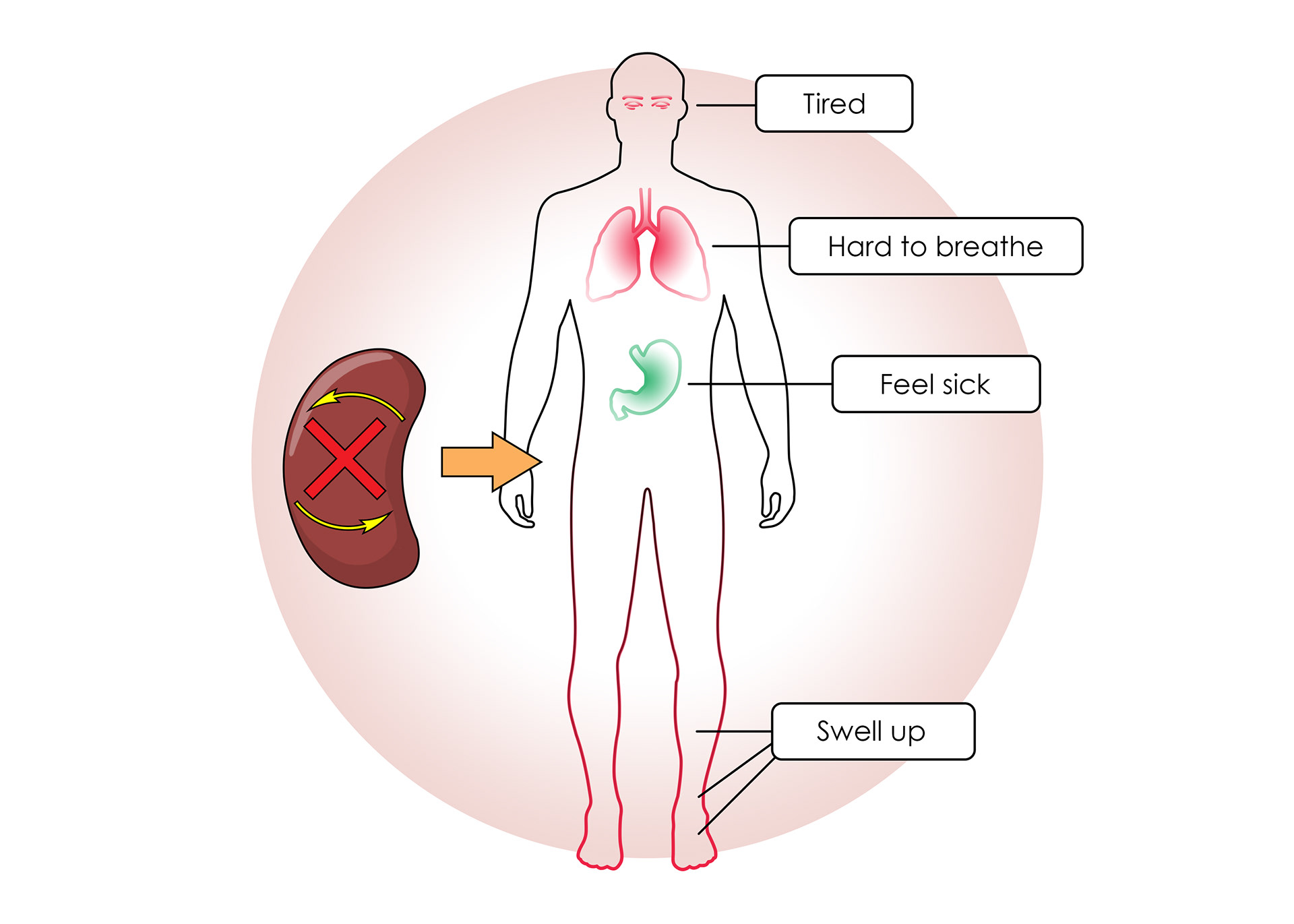
If they don't work properly toxins build up in the body
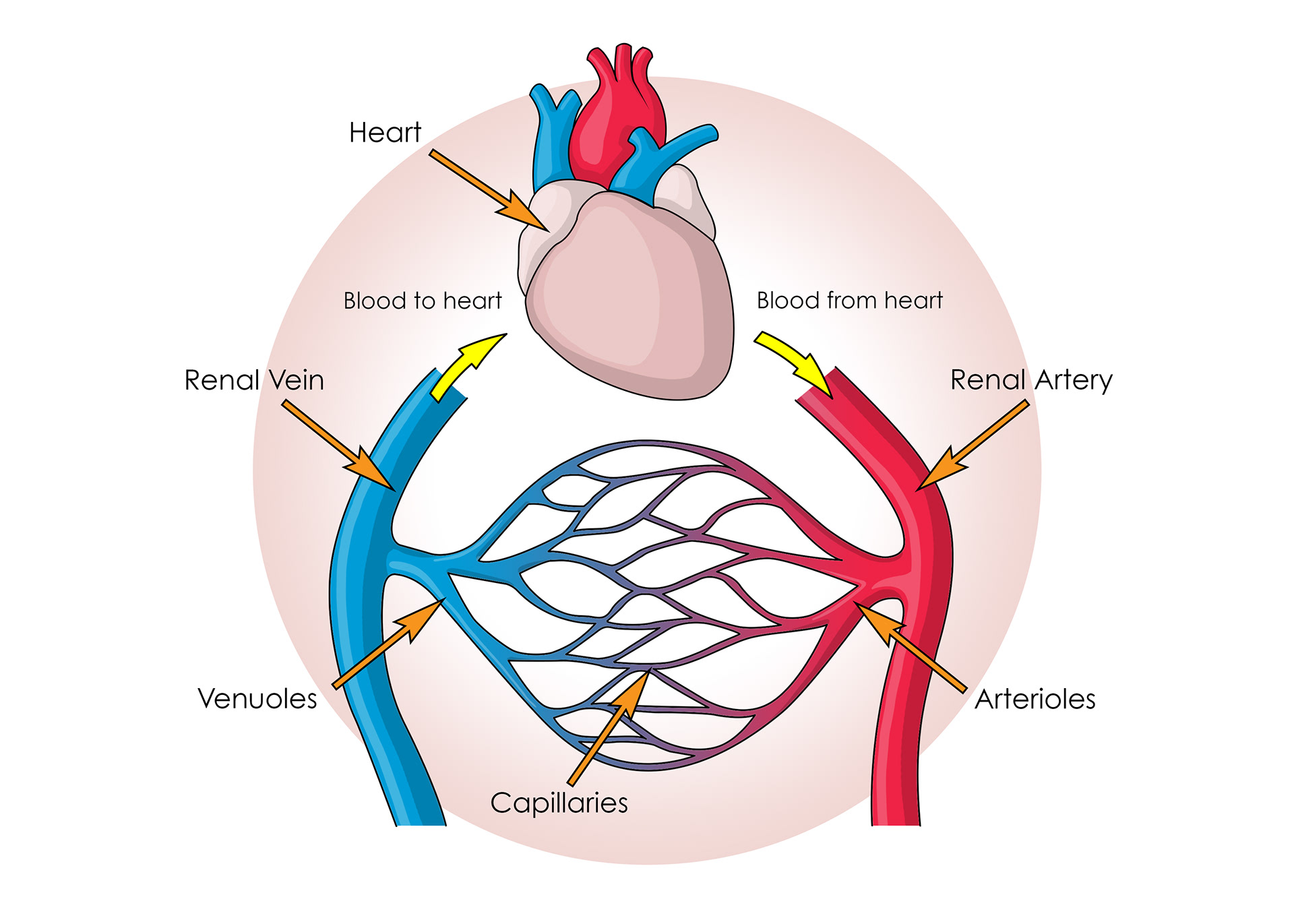
Branching of renal artery into capillaries
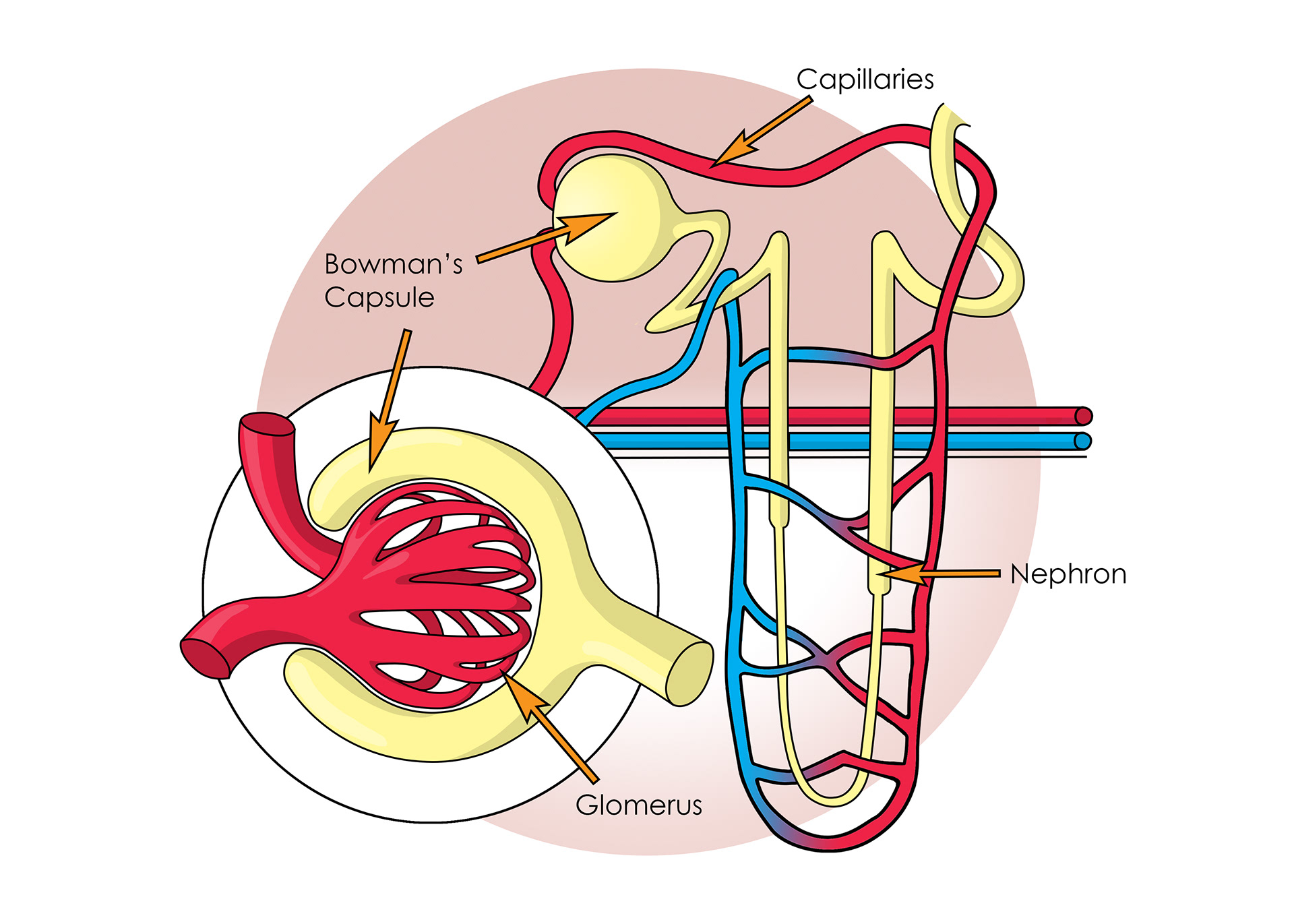
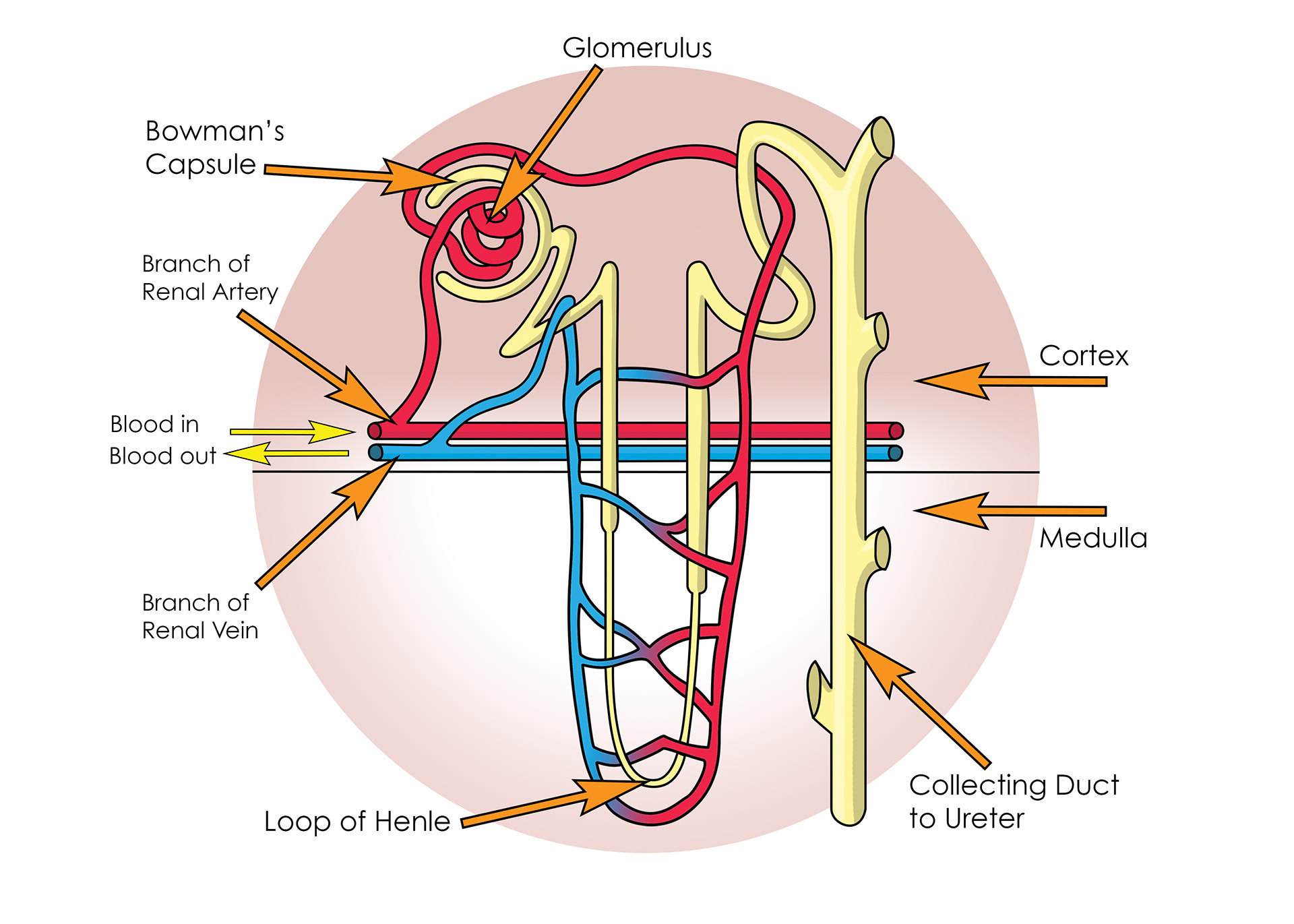
Bowman's Capsule
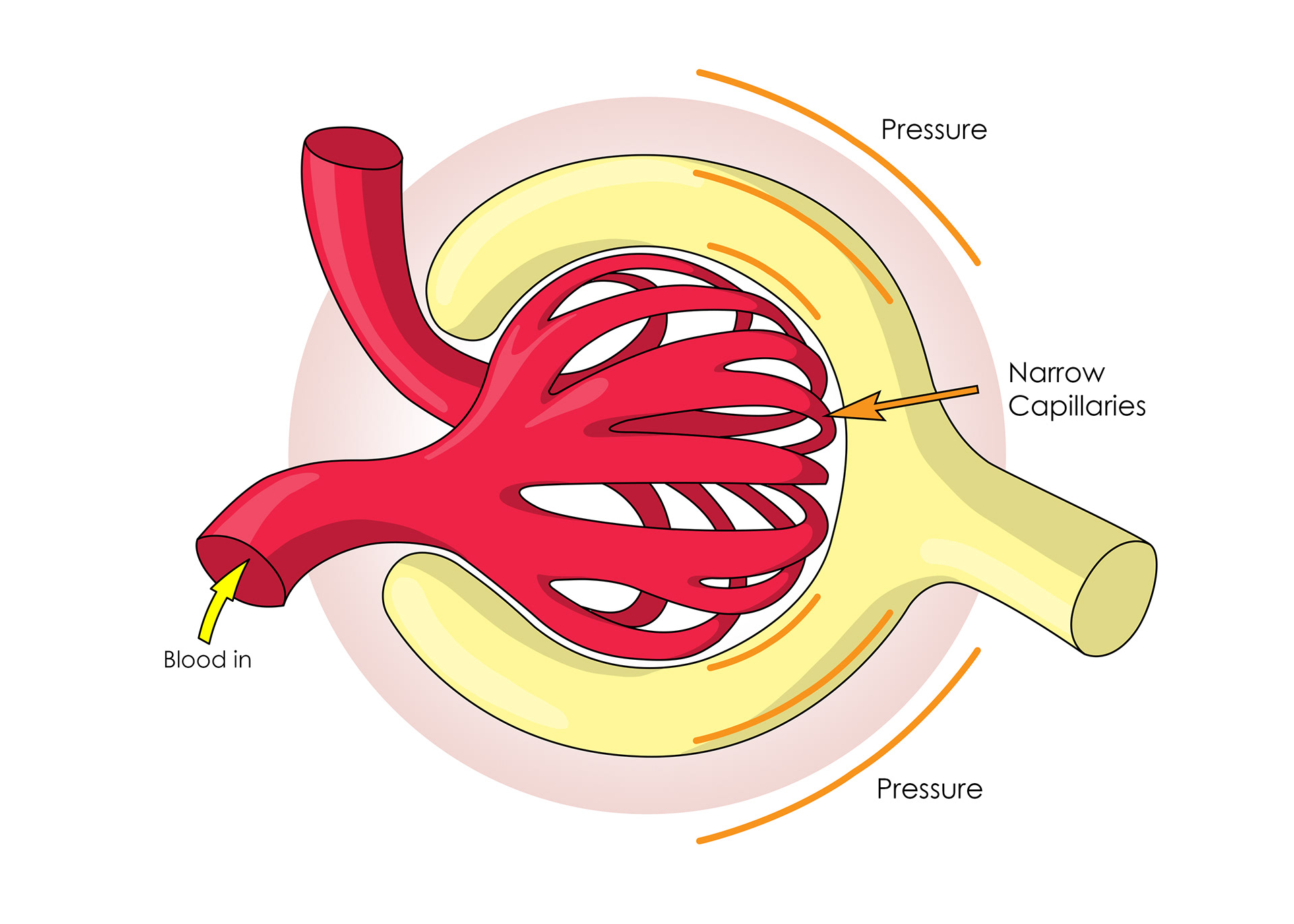
The glomerus
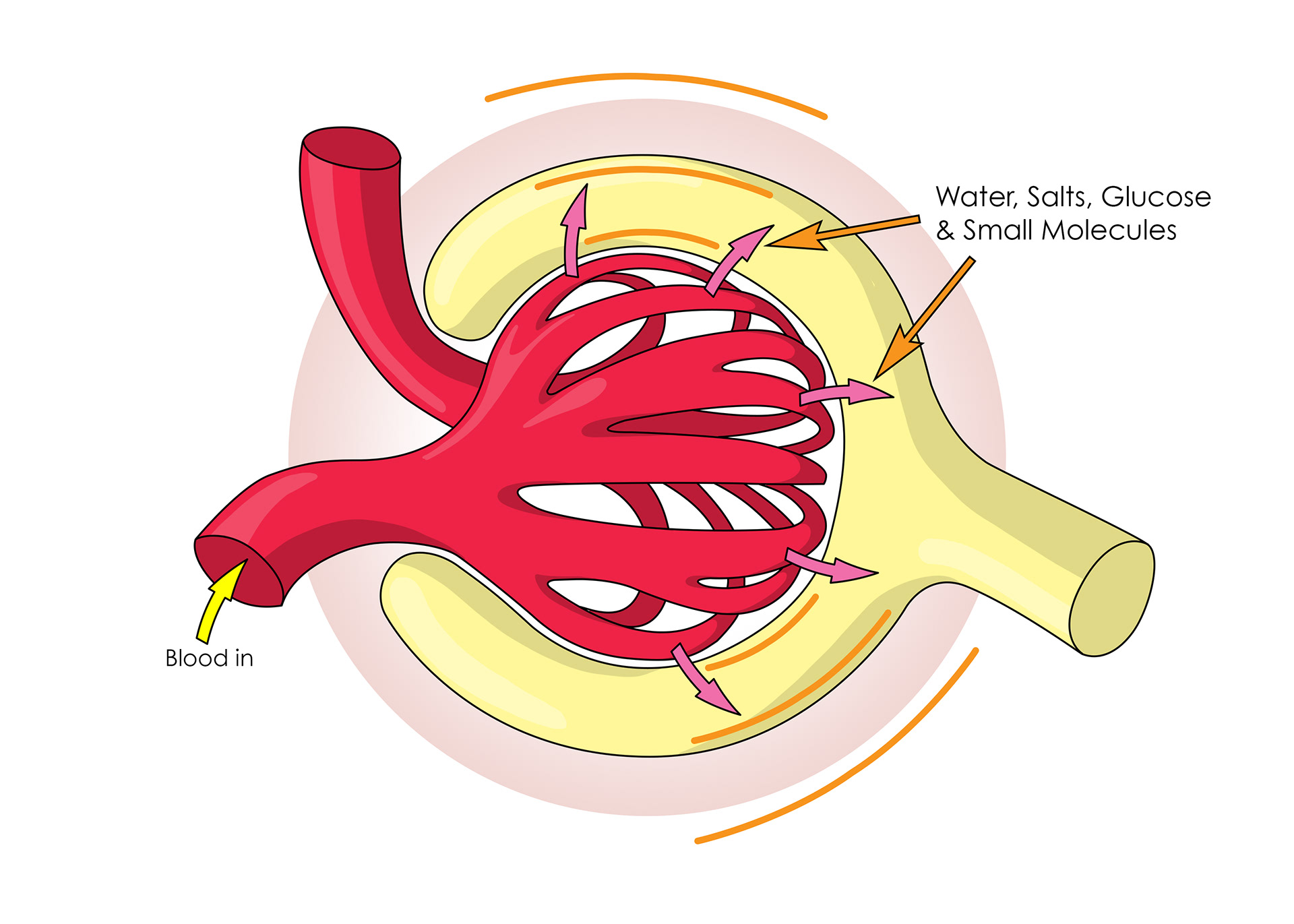
Pressure in capillaries causes ultra filtration
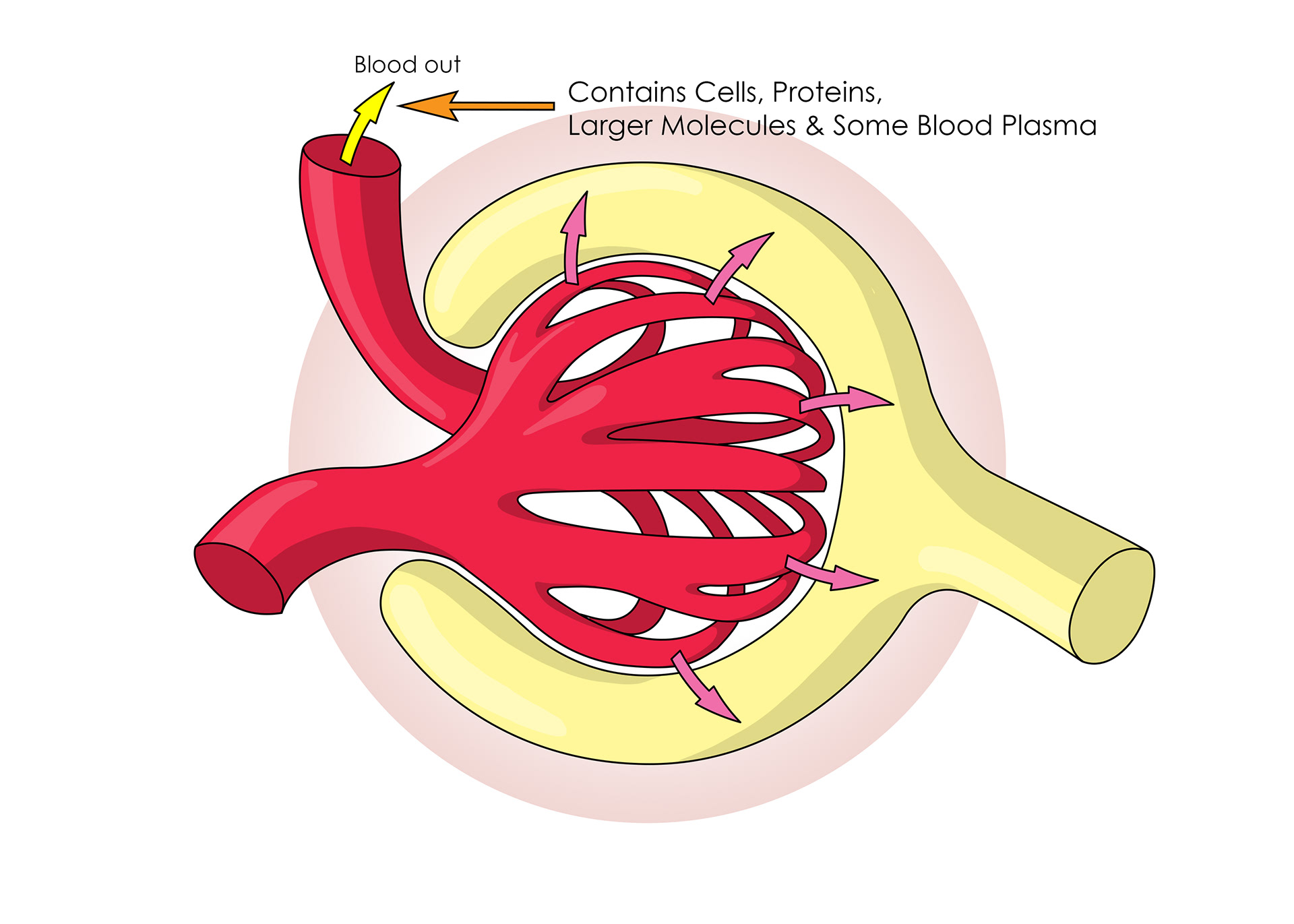
Blood containing larger molecules & proteins leaves through the capillaries
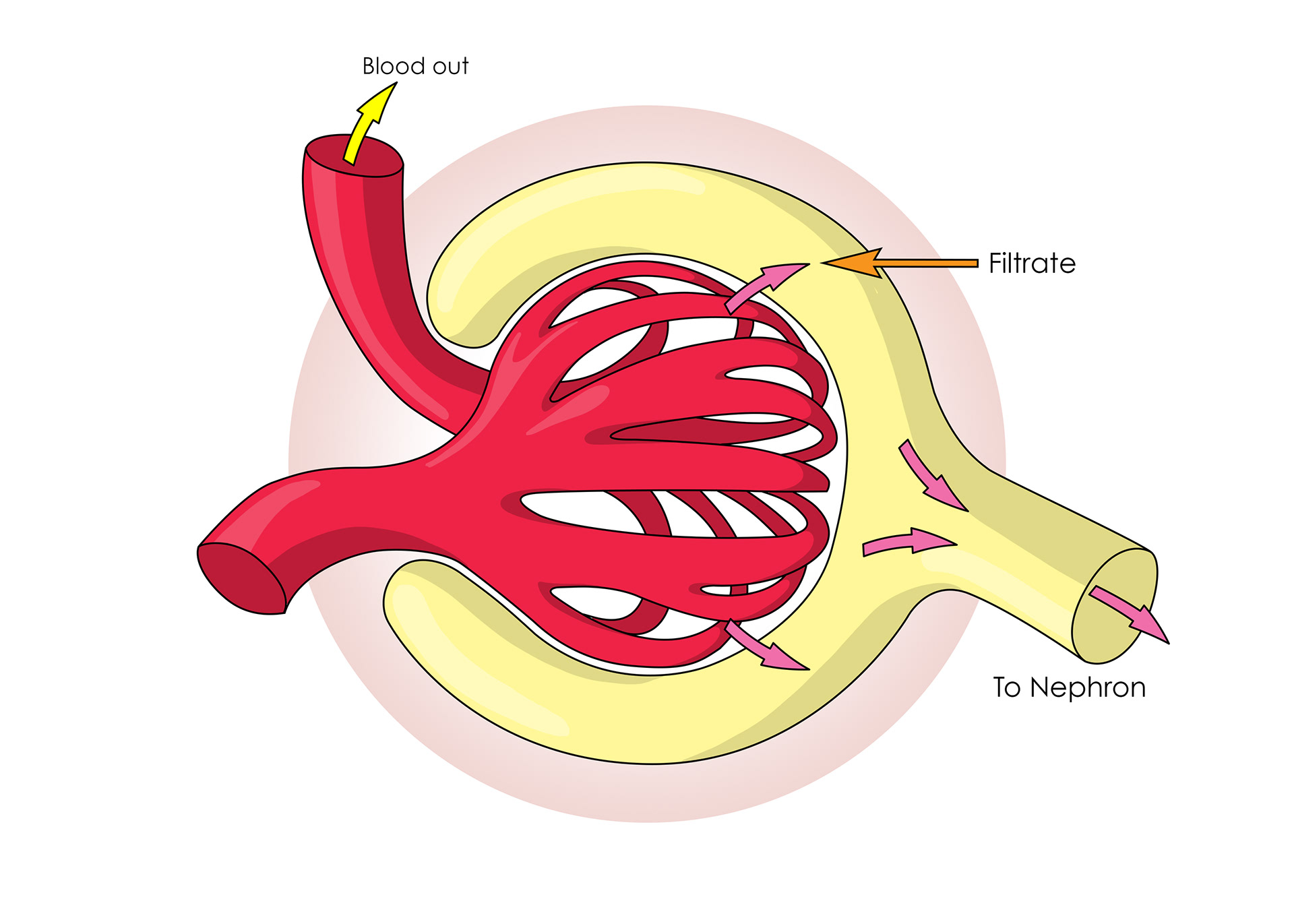
The liquid forced out is called the filtrate
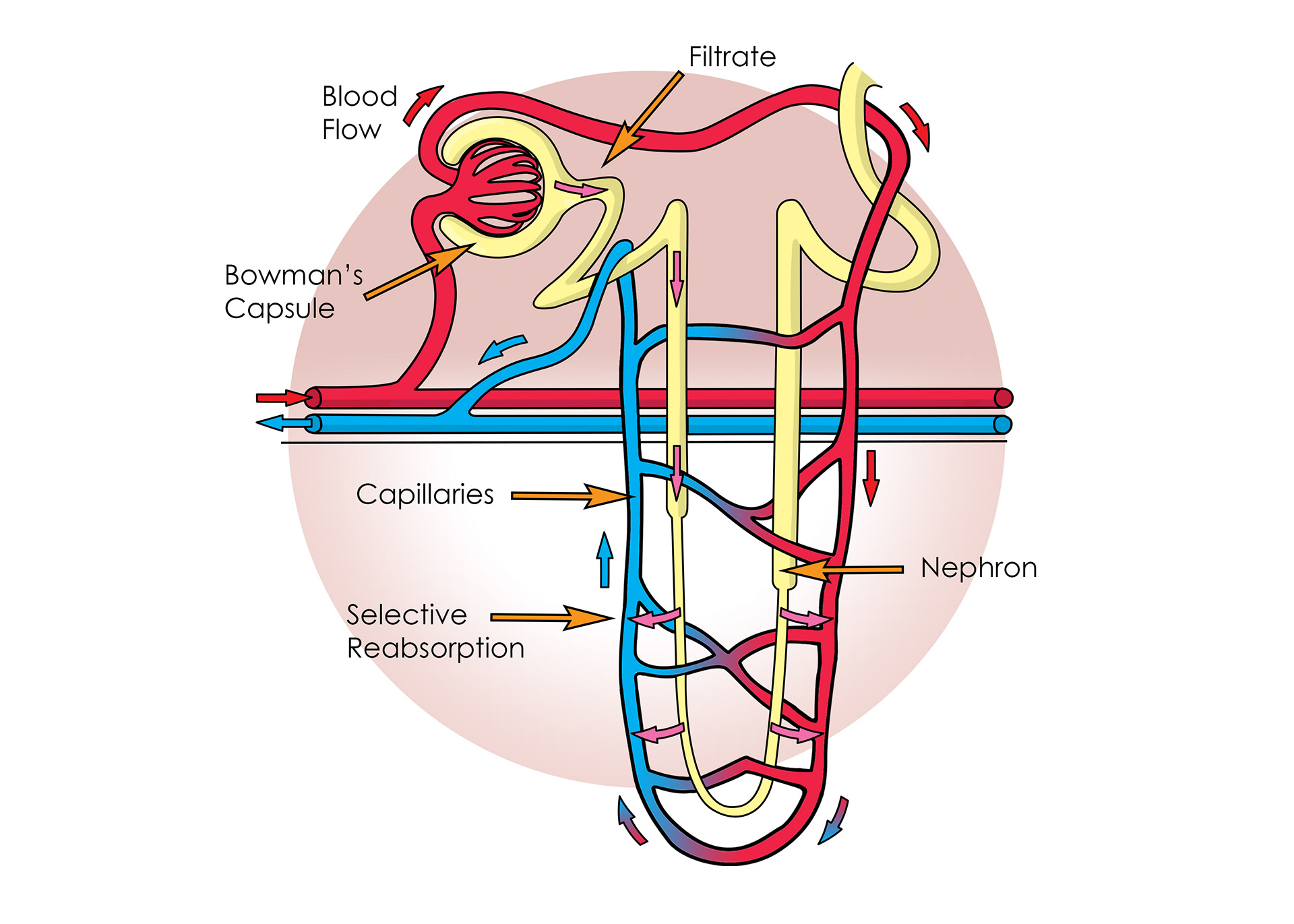
Selective reabsorption of useful things back into capillaries

The loop of henle
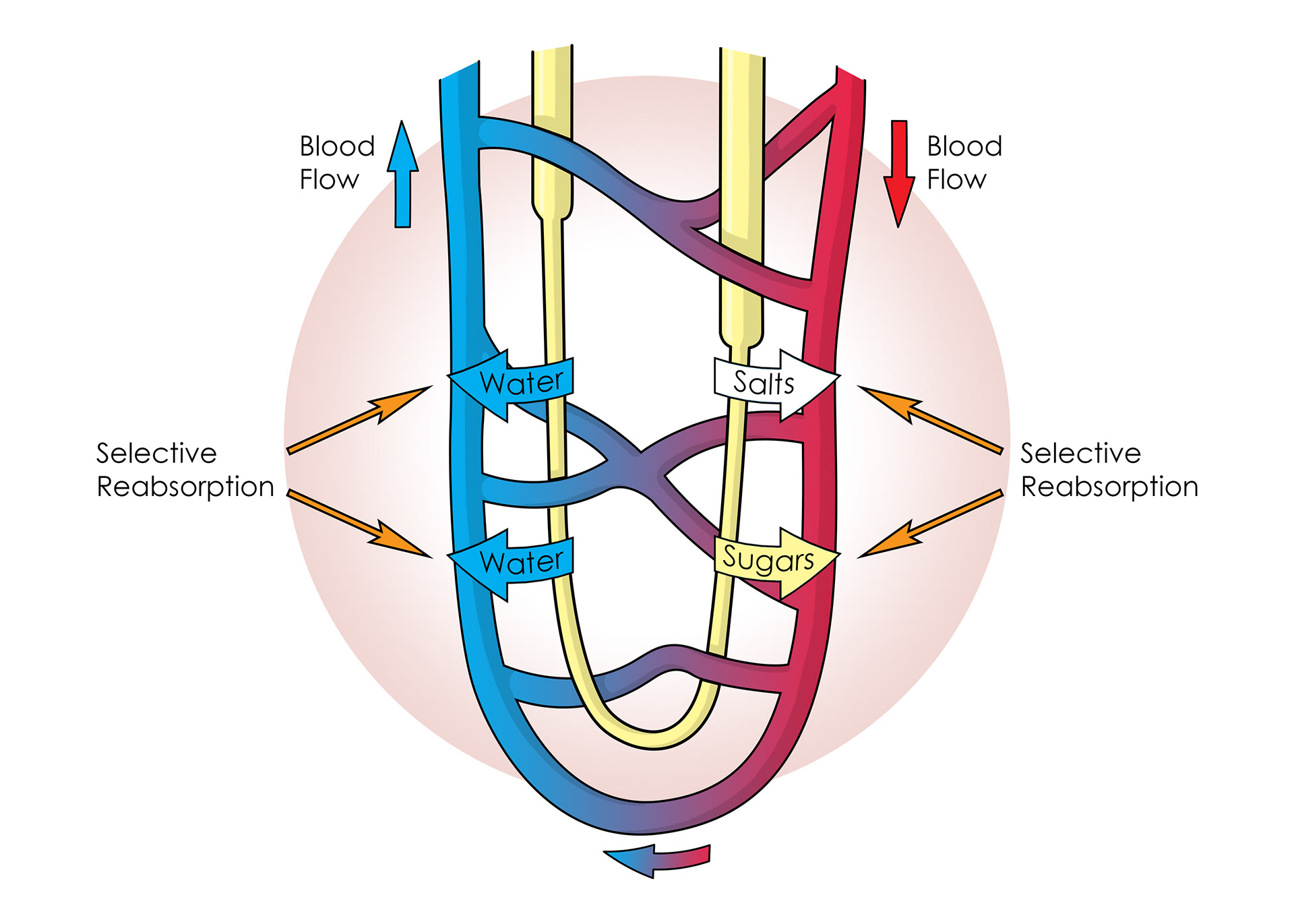
Glucose, salts & water selectively reabsorbed
The nephrons control how much water, sugar & salt the body loses
Changing the amount of water in the blood affects blood pressure

Sweating affects the amount of water in the blood

Diet - also affects water reabsorption
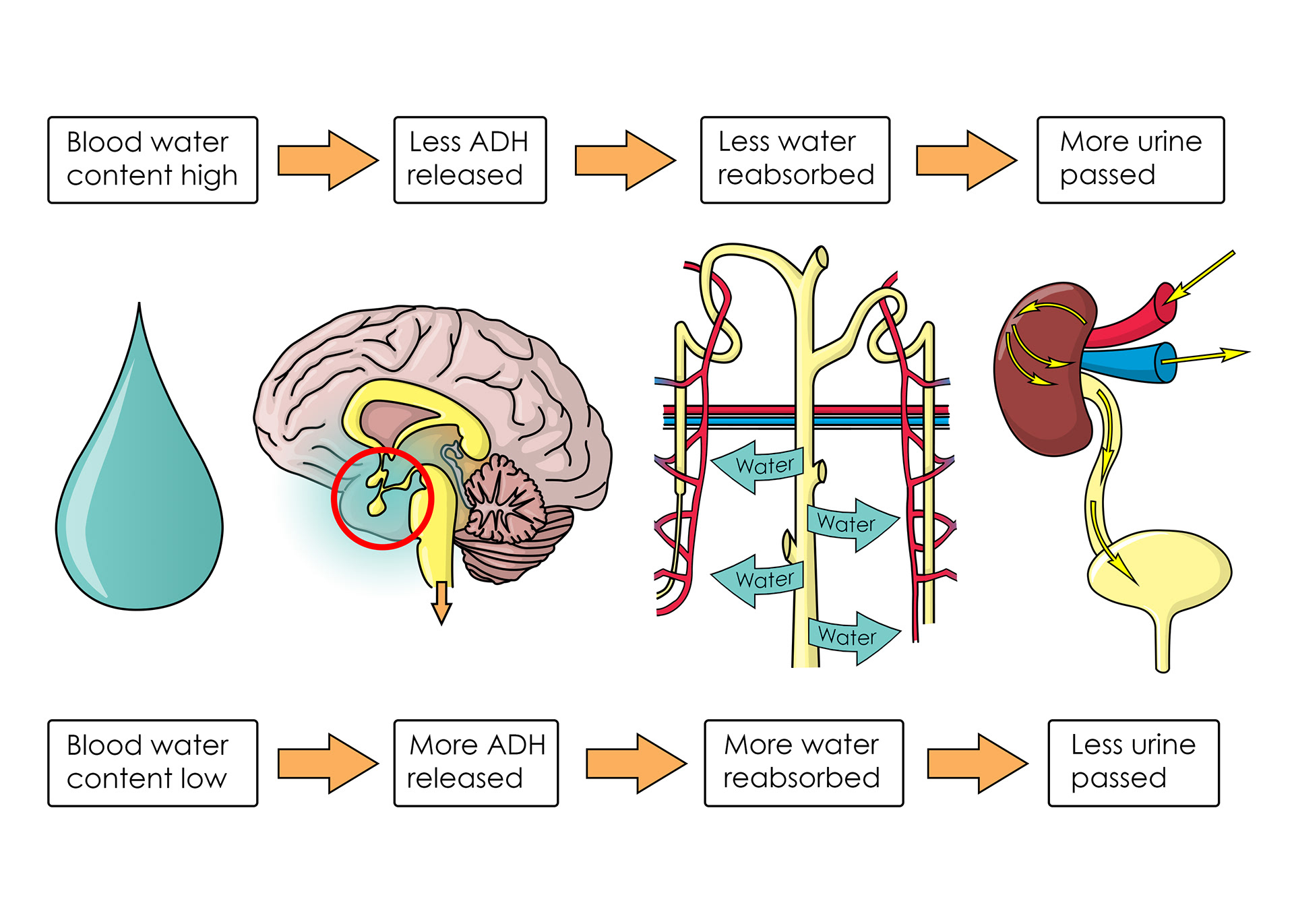
Anti-diuretic hormone helps regulate water reabsorption
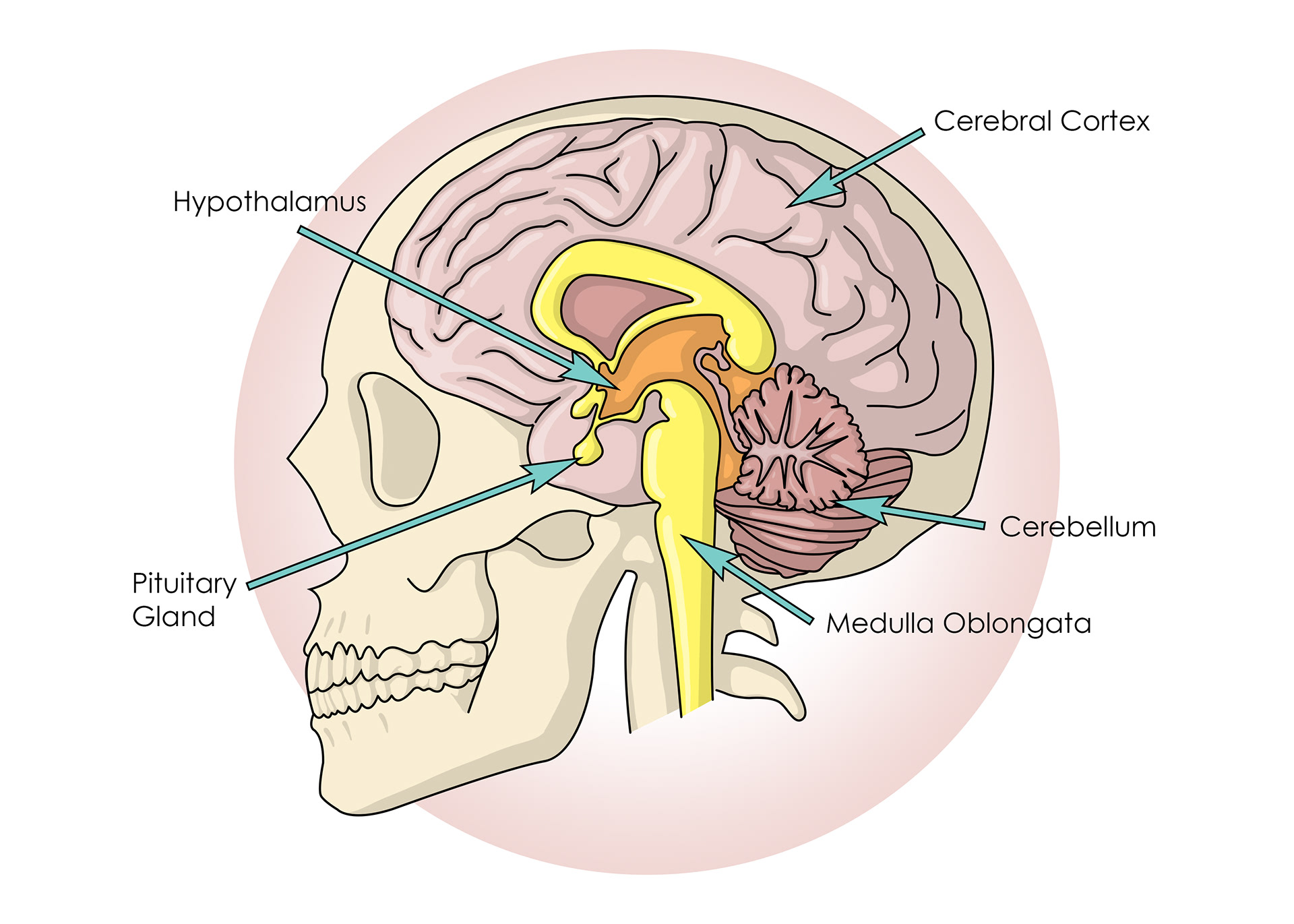
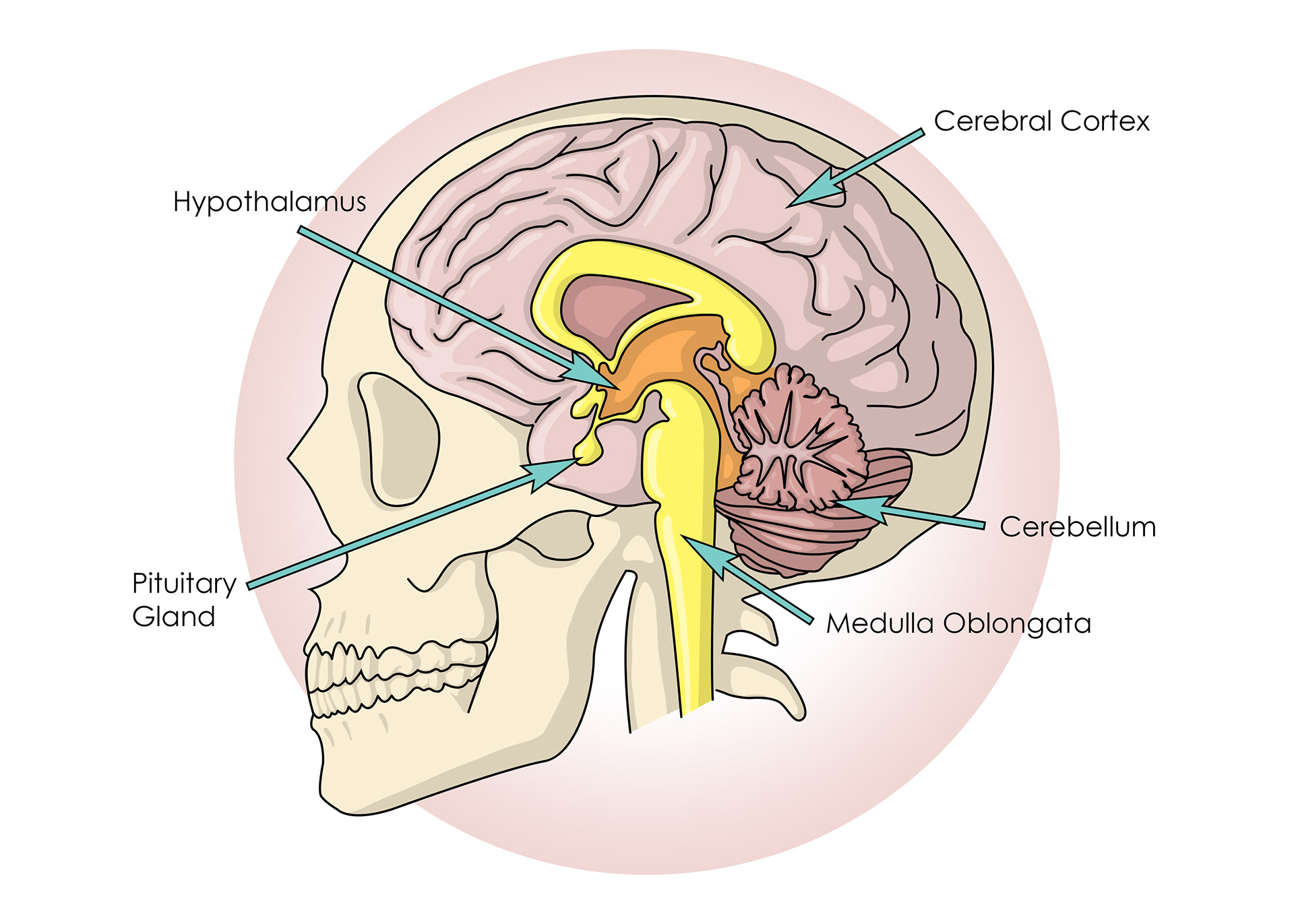
The brain
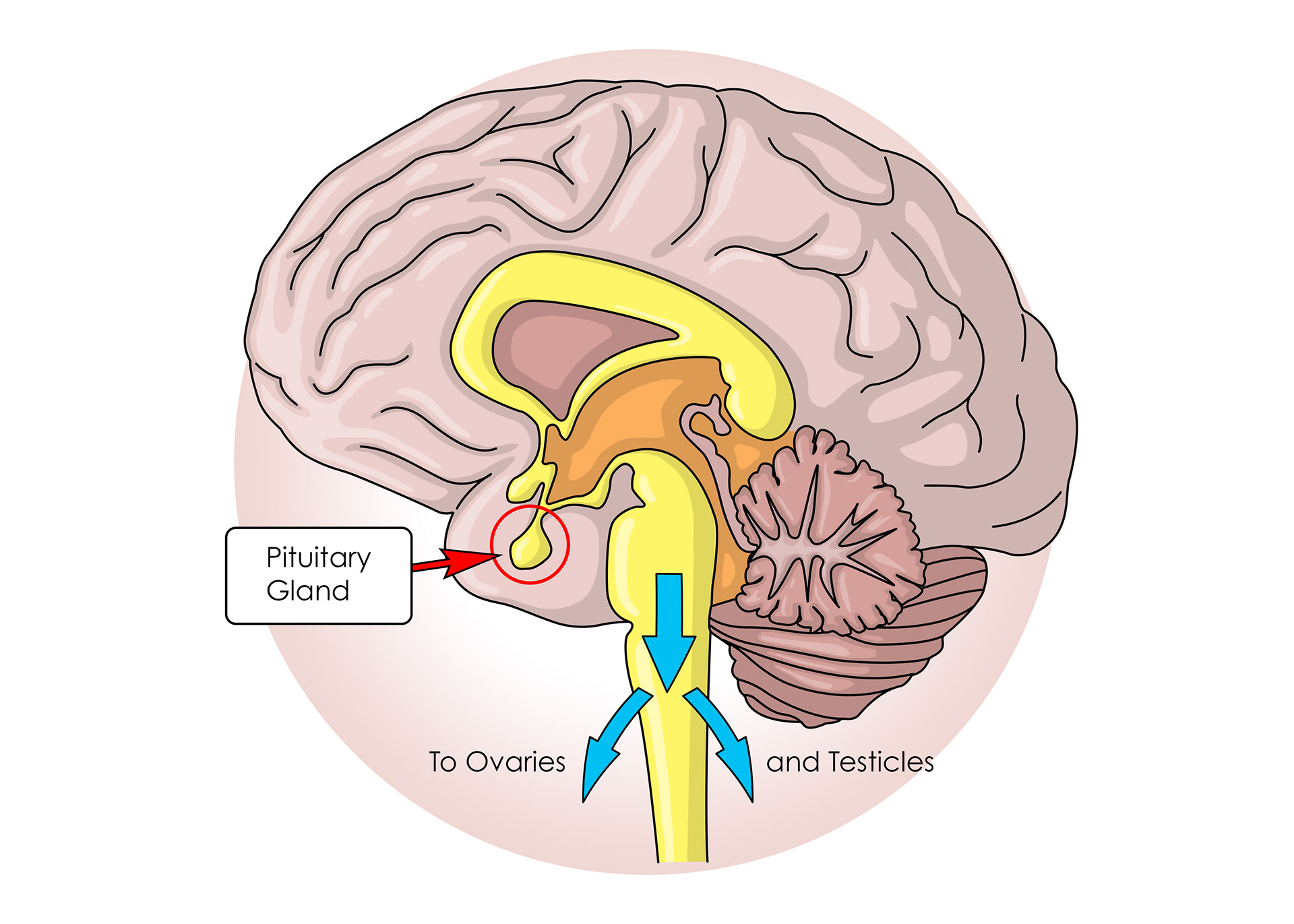
ADH from the pituitary gland travels in the blood
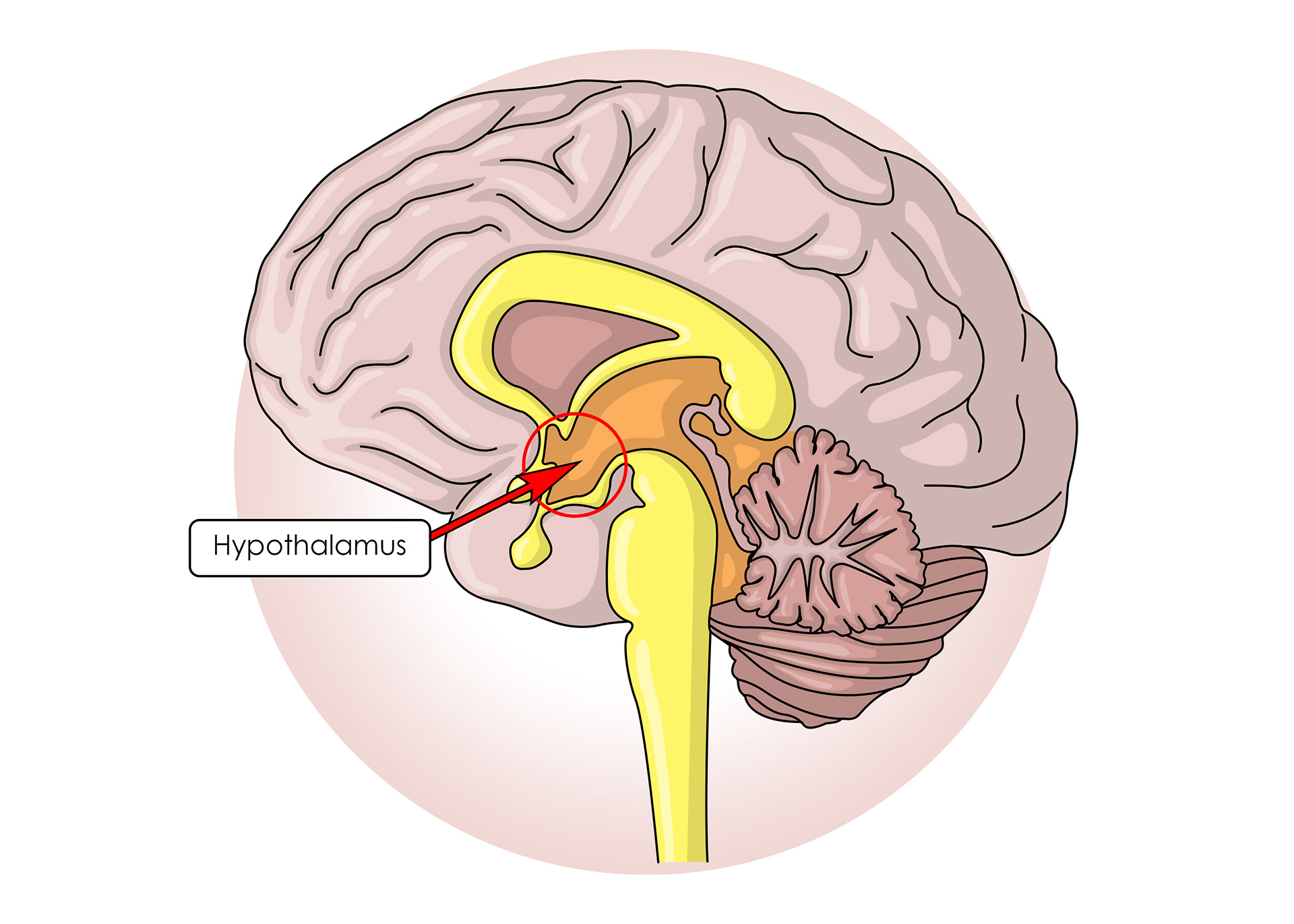
Hypothalamus - controls the pituitary gland
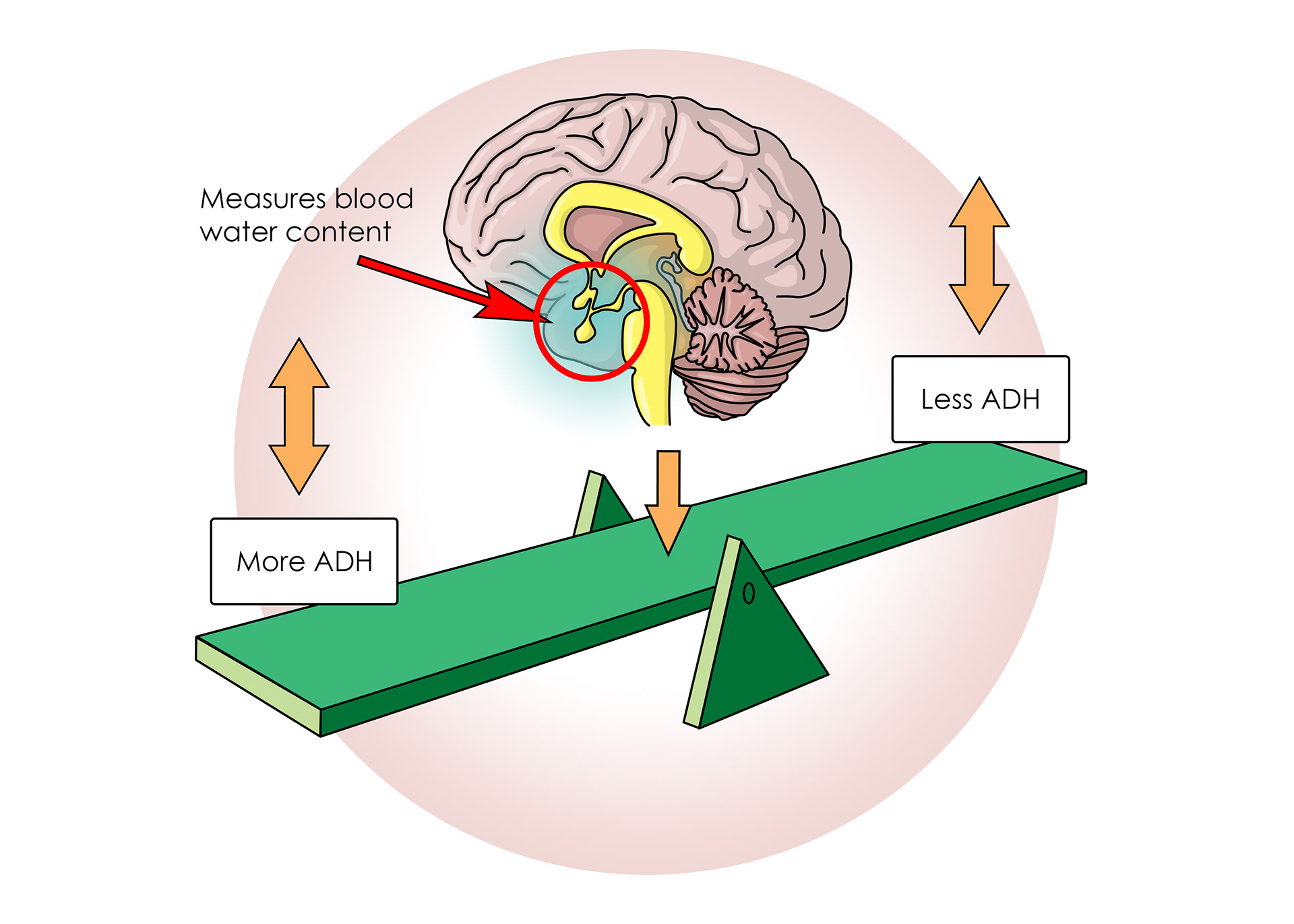
The hypothalamus measure how much water is in the blood
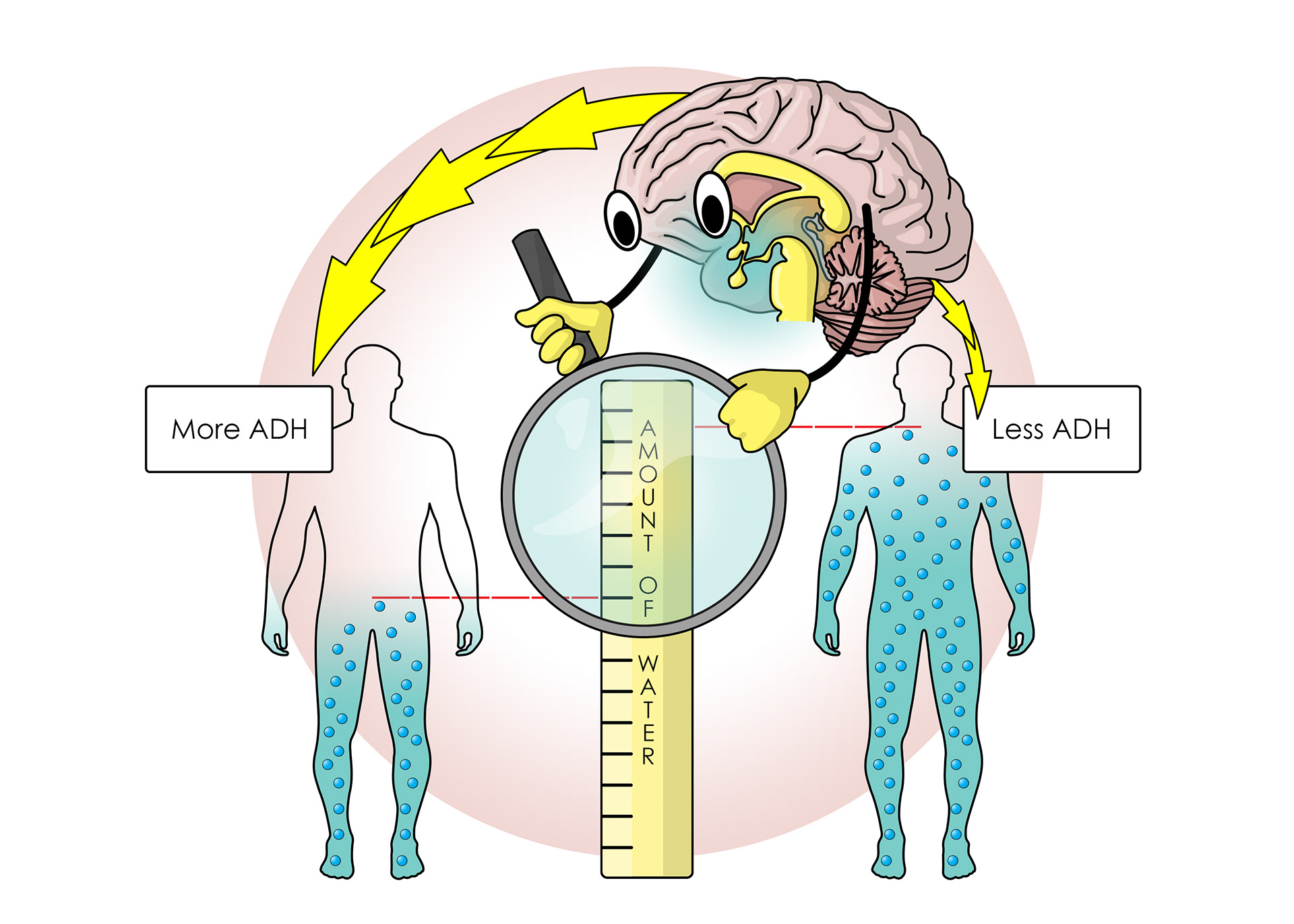
Example of negative feedback

Sometimes kidneys don't work as they should - kidney disease. If they stop working it is called kidney failure
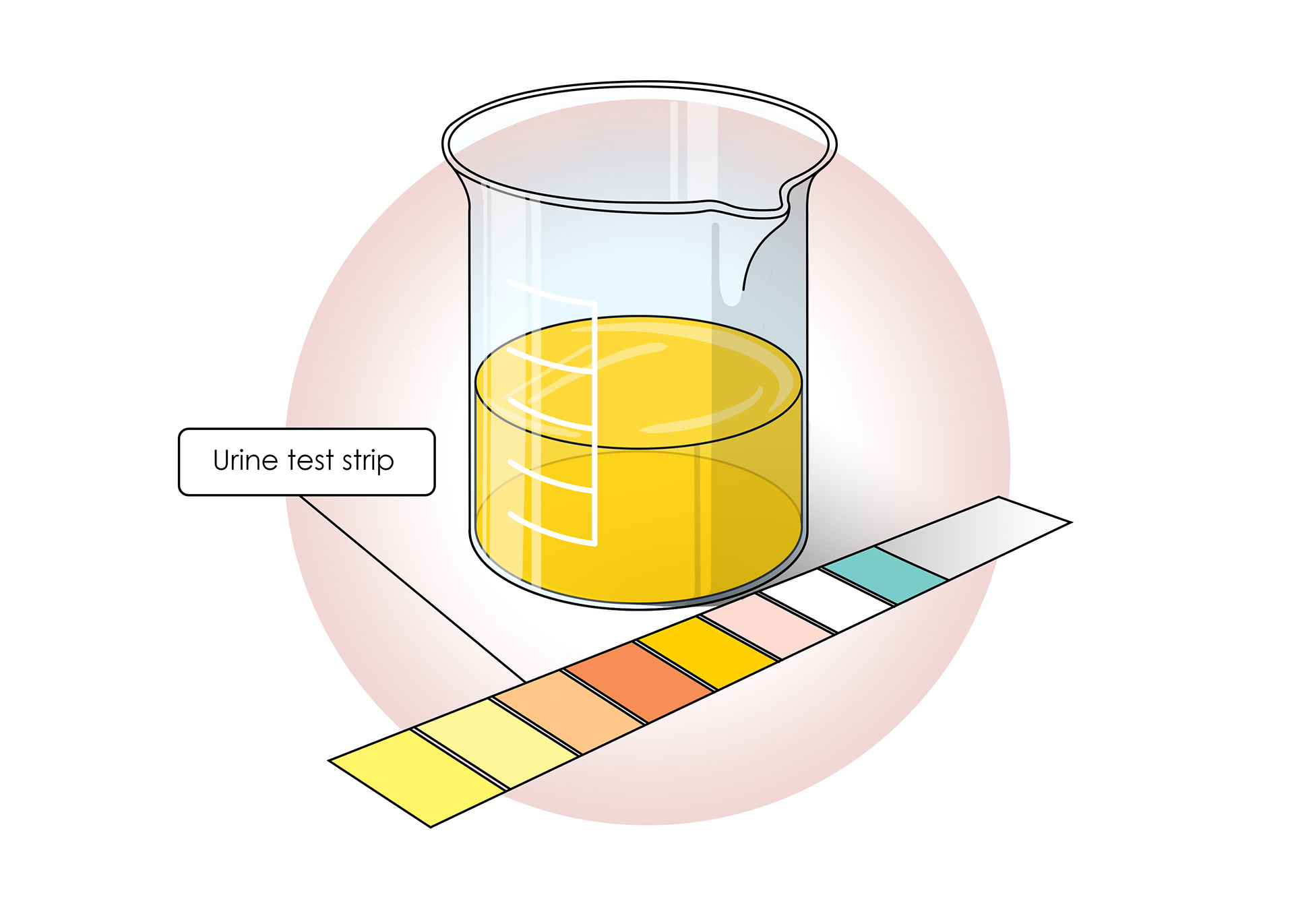
Testing urine can check if the kidneys are working properly
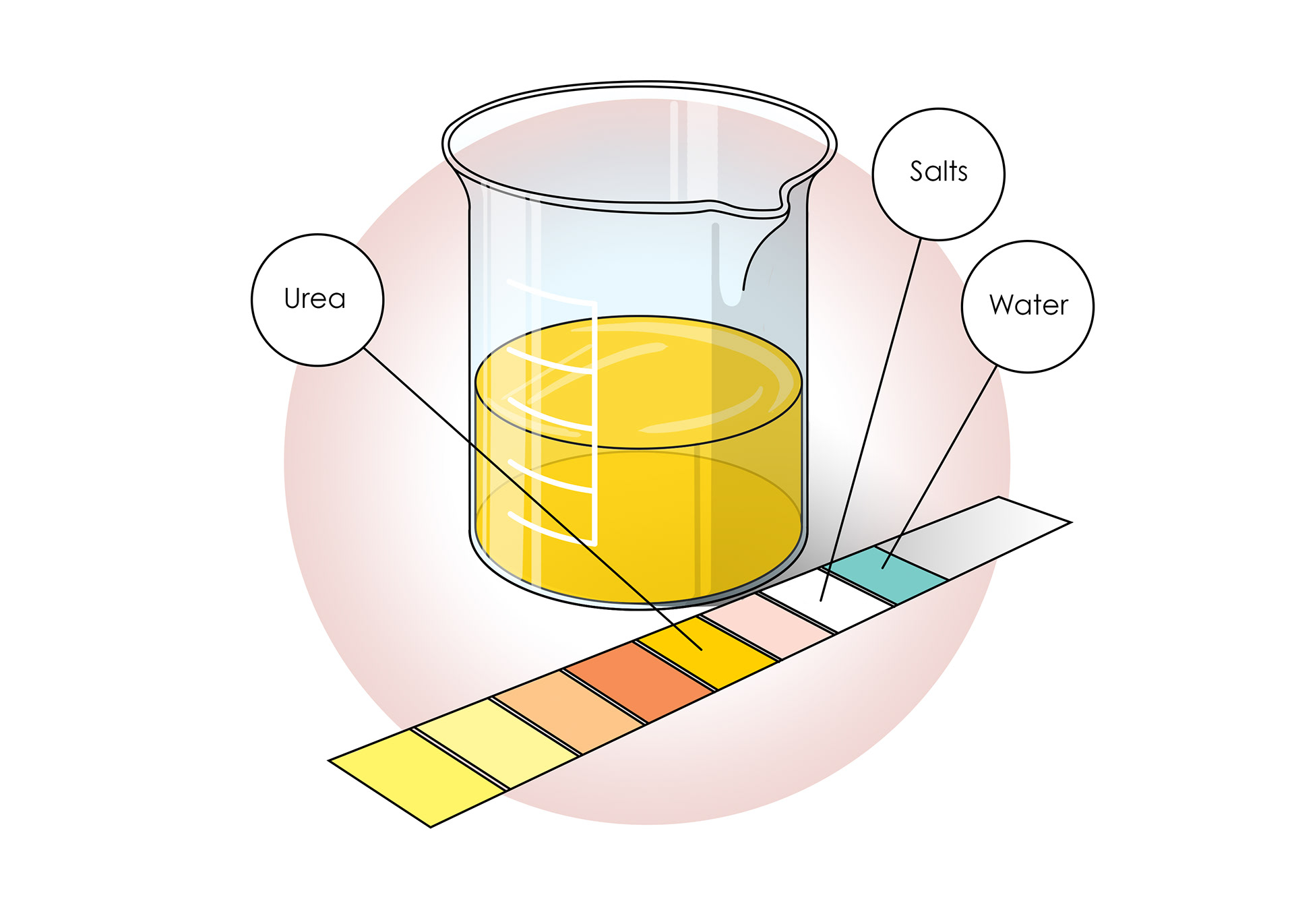
Urine should only contain waste products
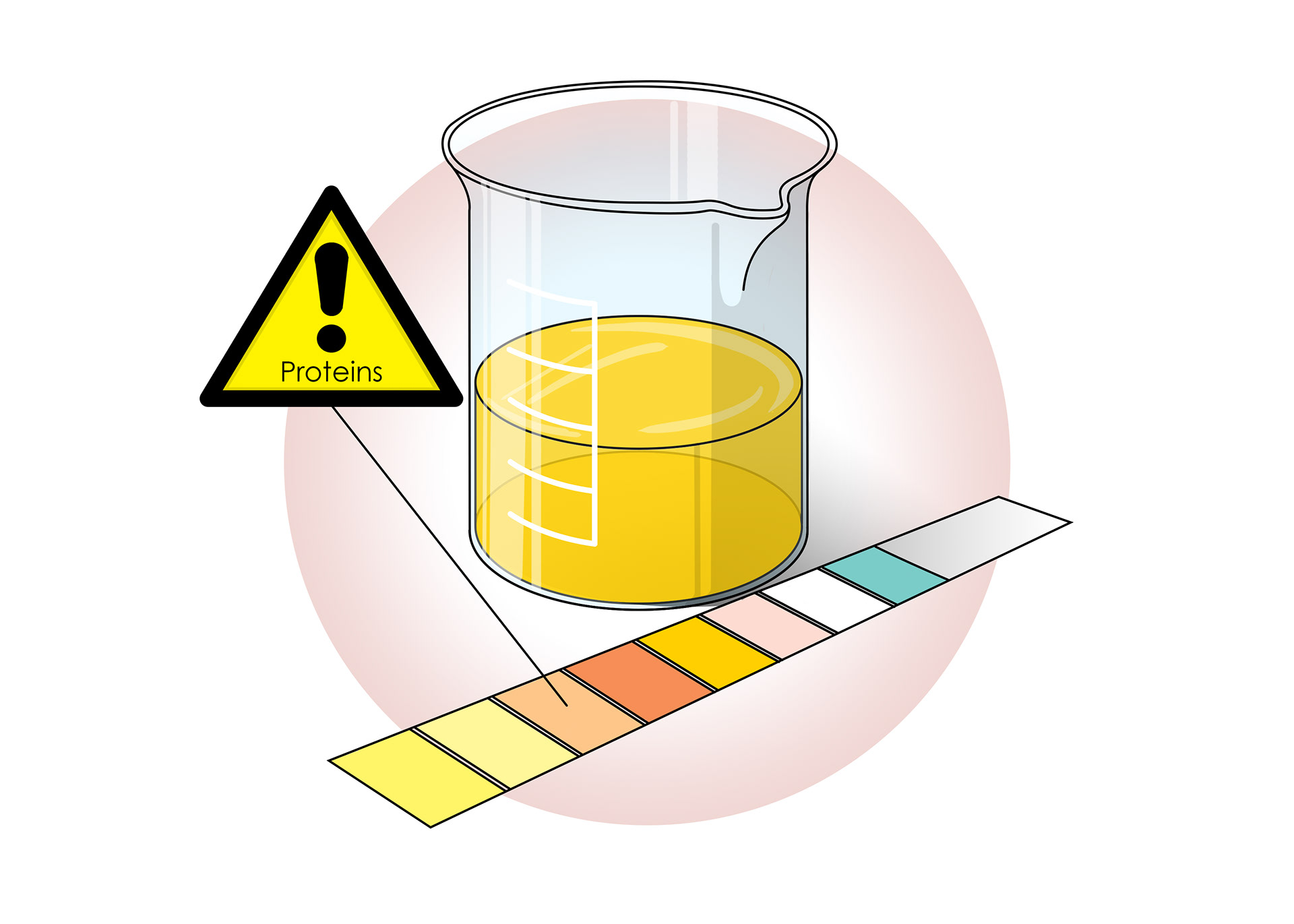
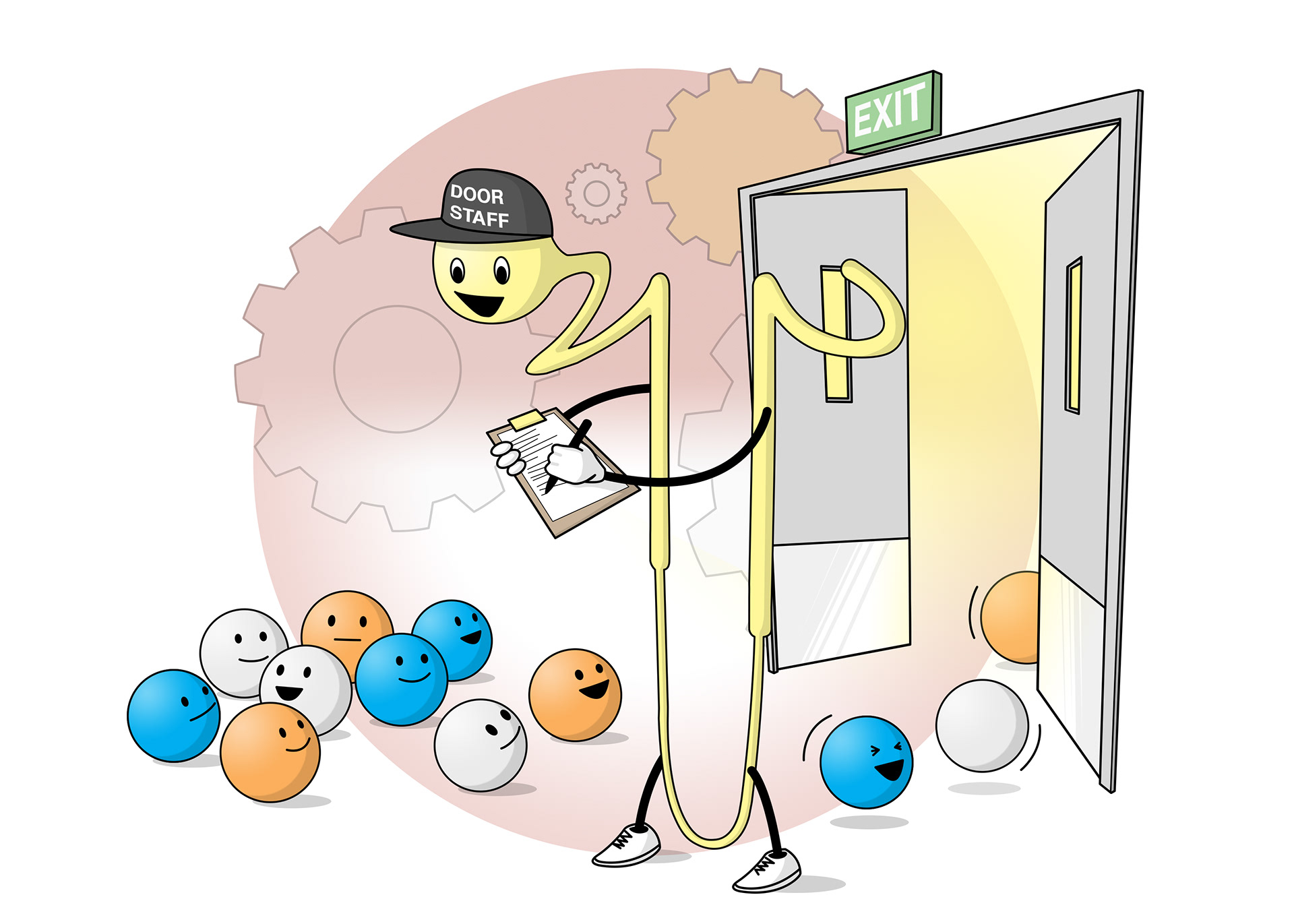
Proteins and cells are too big to move into the nephrons - proteins in urine is a bad sign
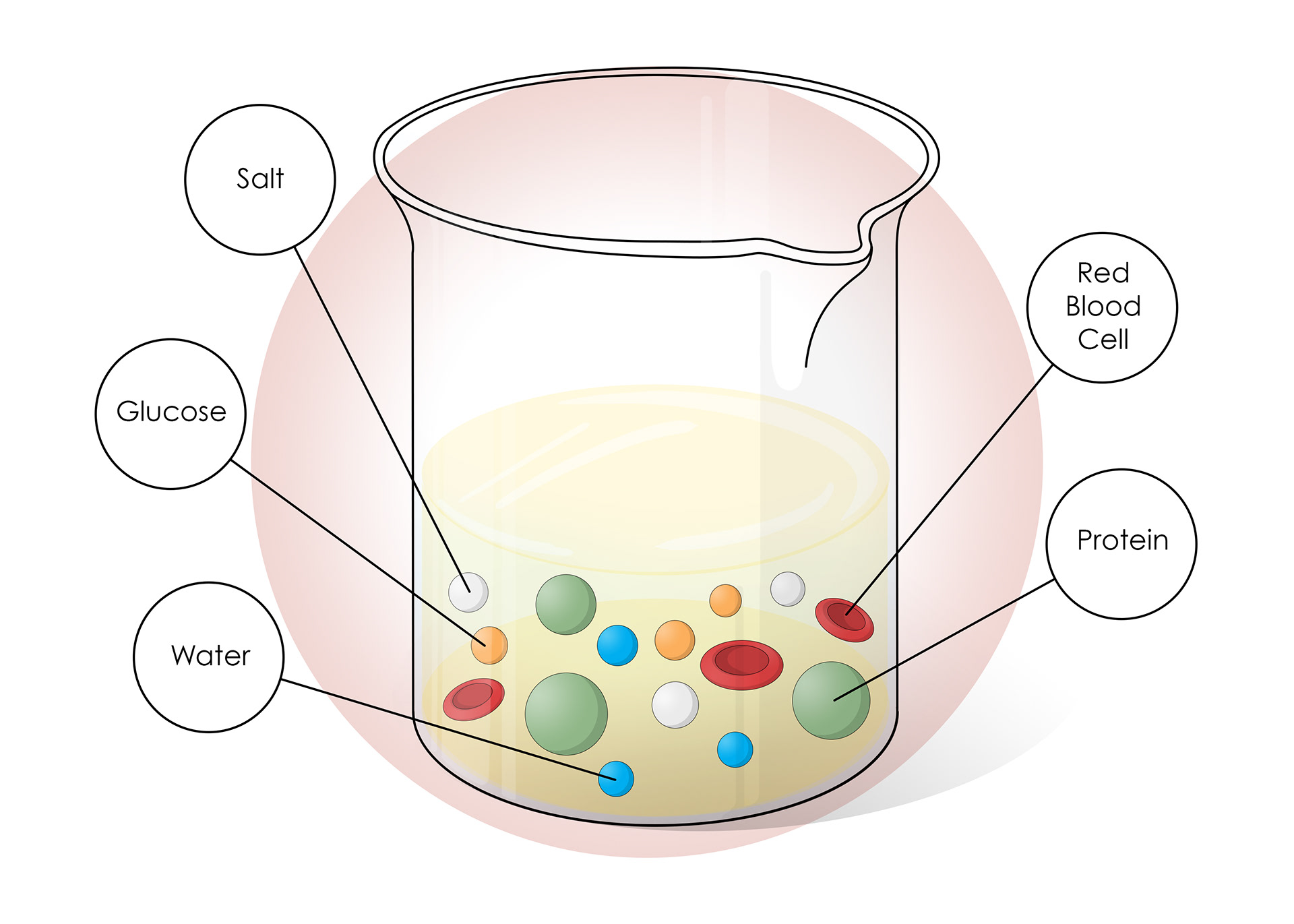
The body wants to retain useful things

Too much glucose can signify diabetes
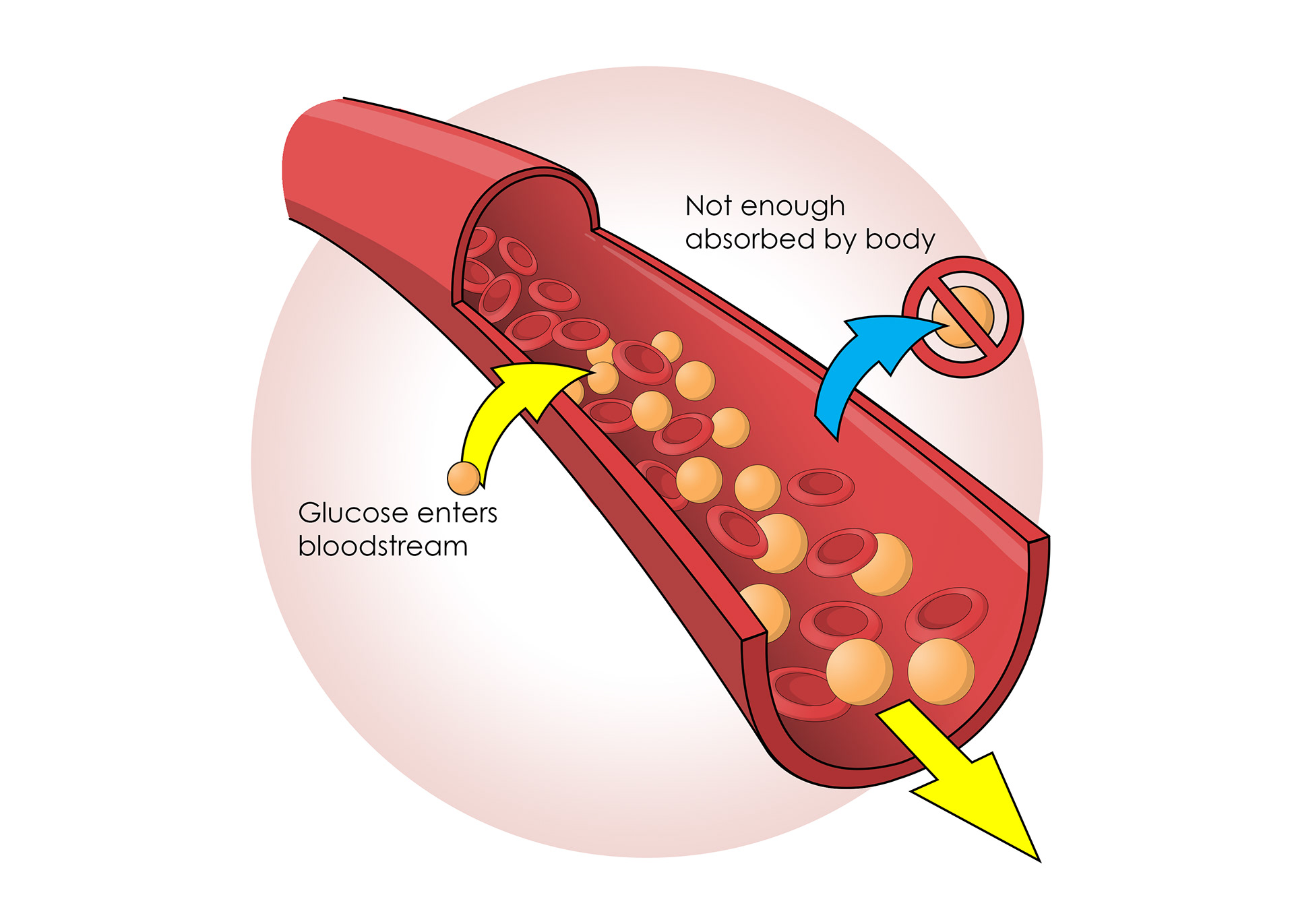
Diabetics can't control the amount of glucose in their blood
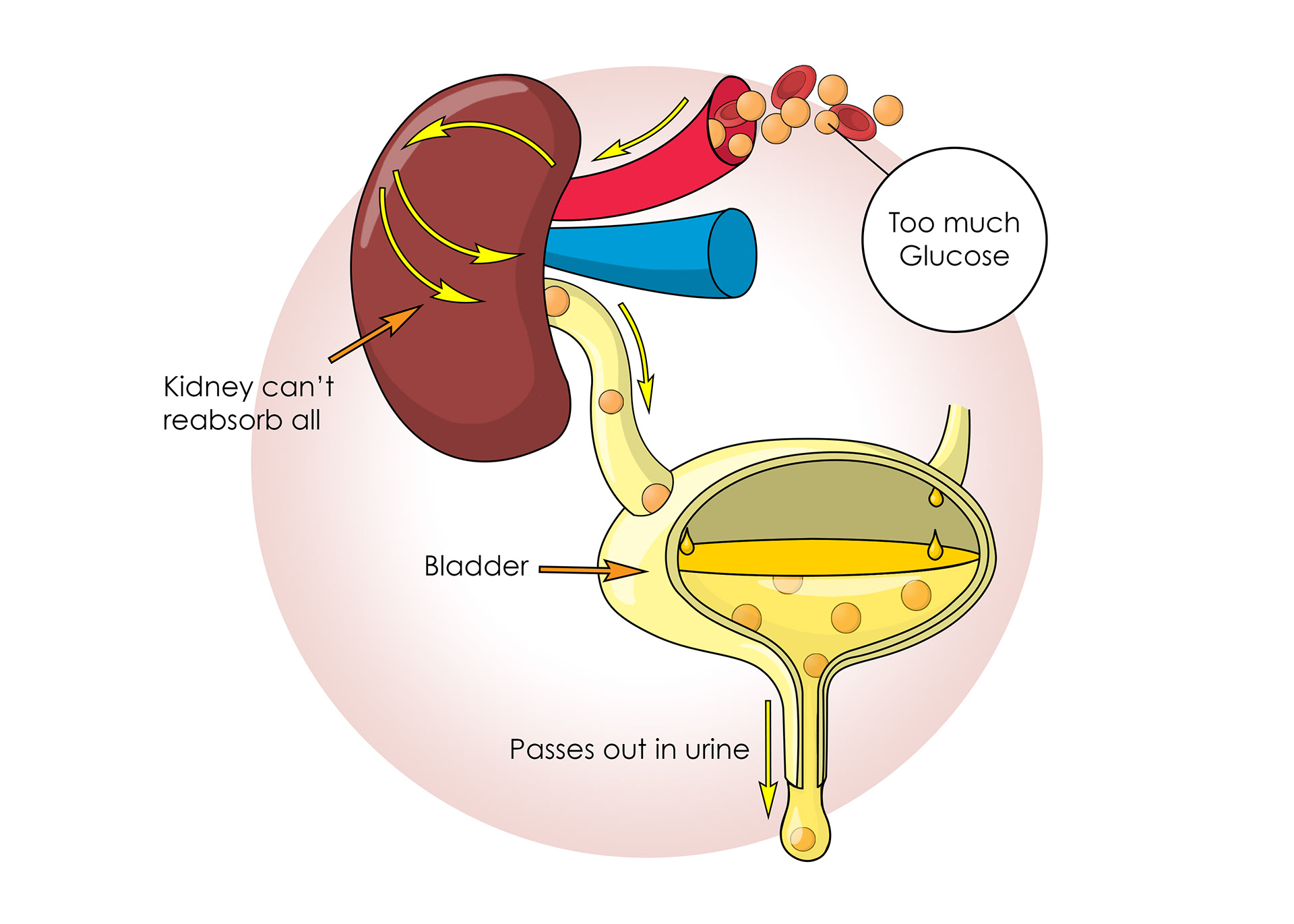
Too much glucose for the body to reabsorb can end up in urine
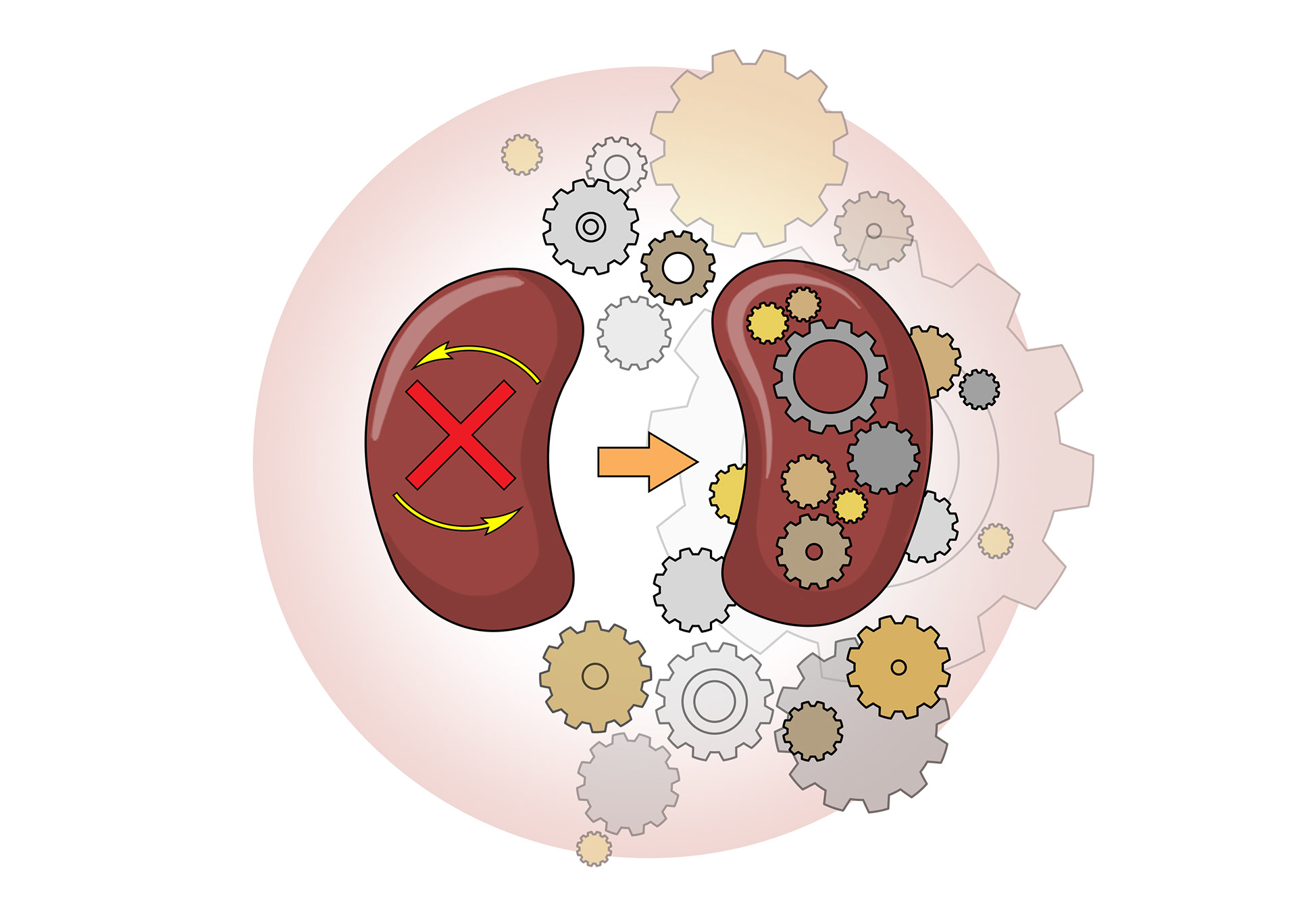
If one kidney stops working the other one has to work harder

If both stop working the person will die if not treated
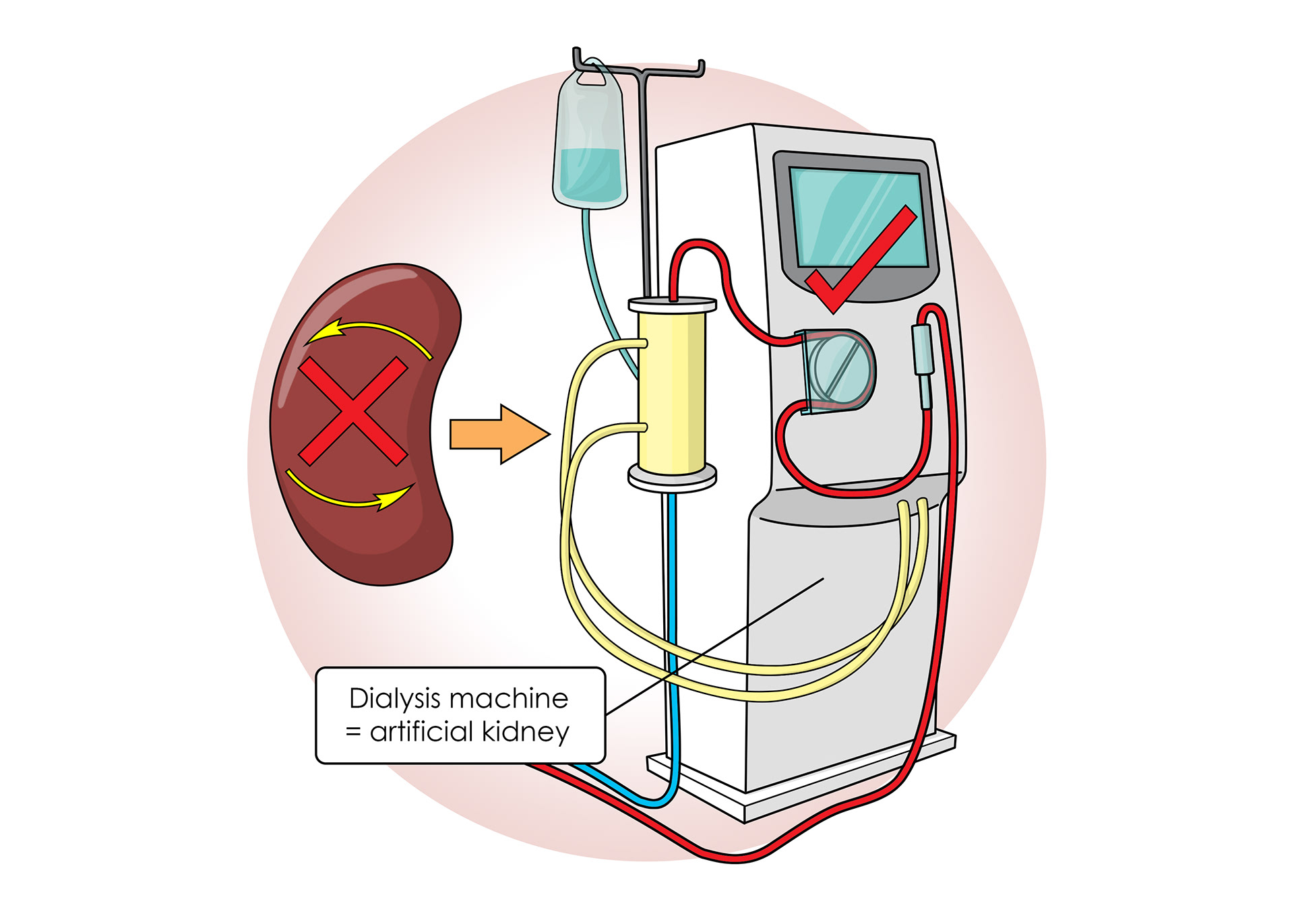
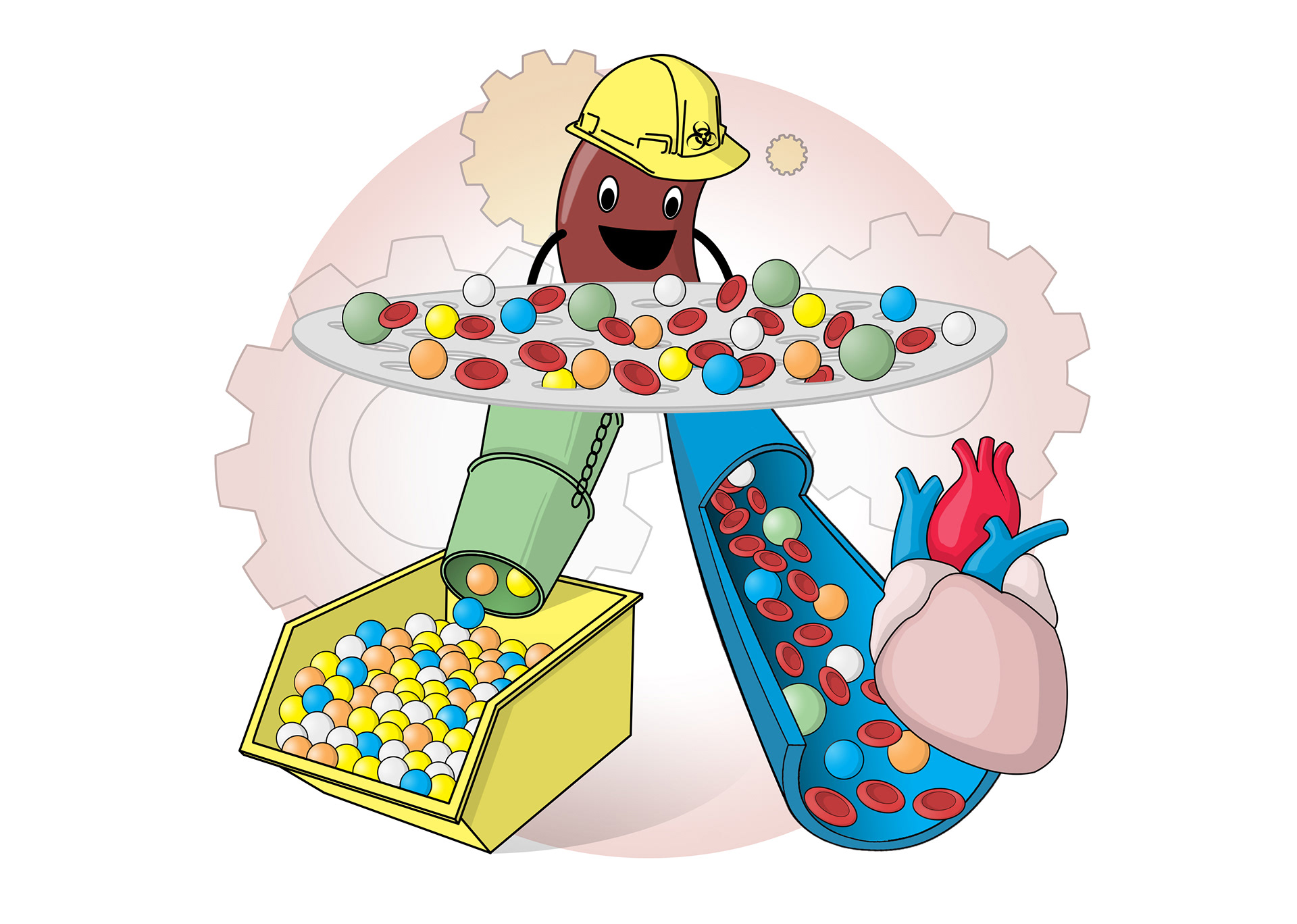
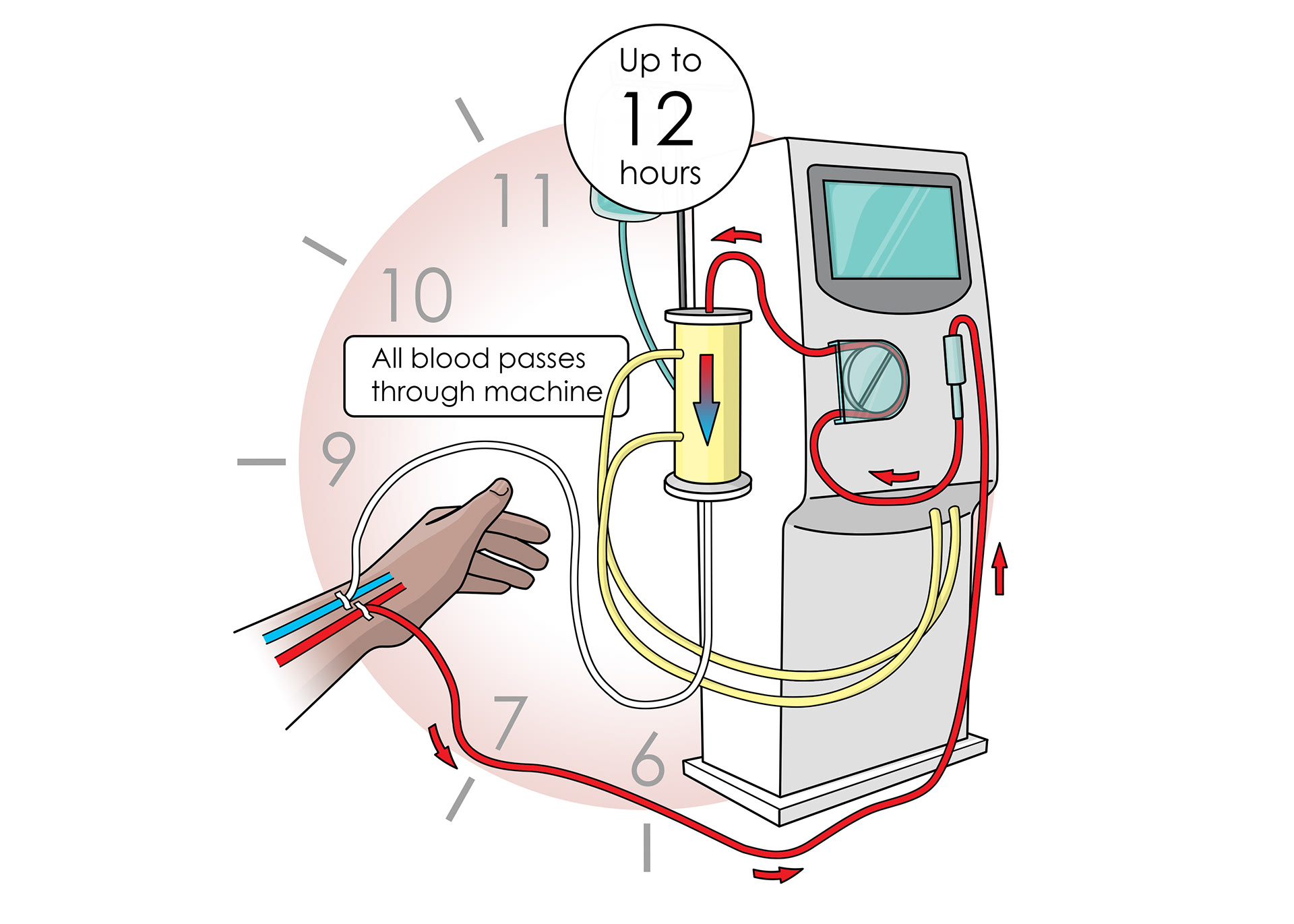
Dialysis machines - artificial kidneys
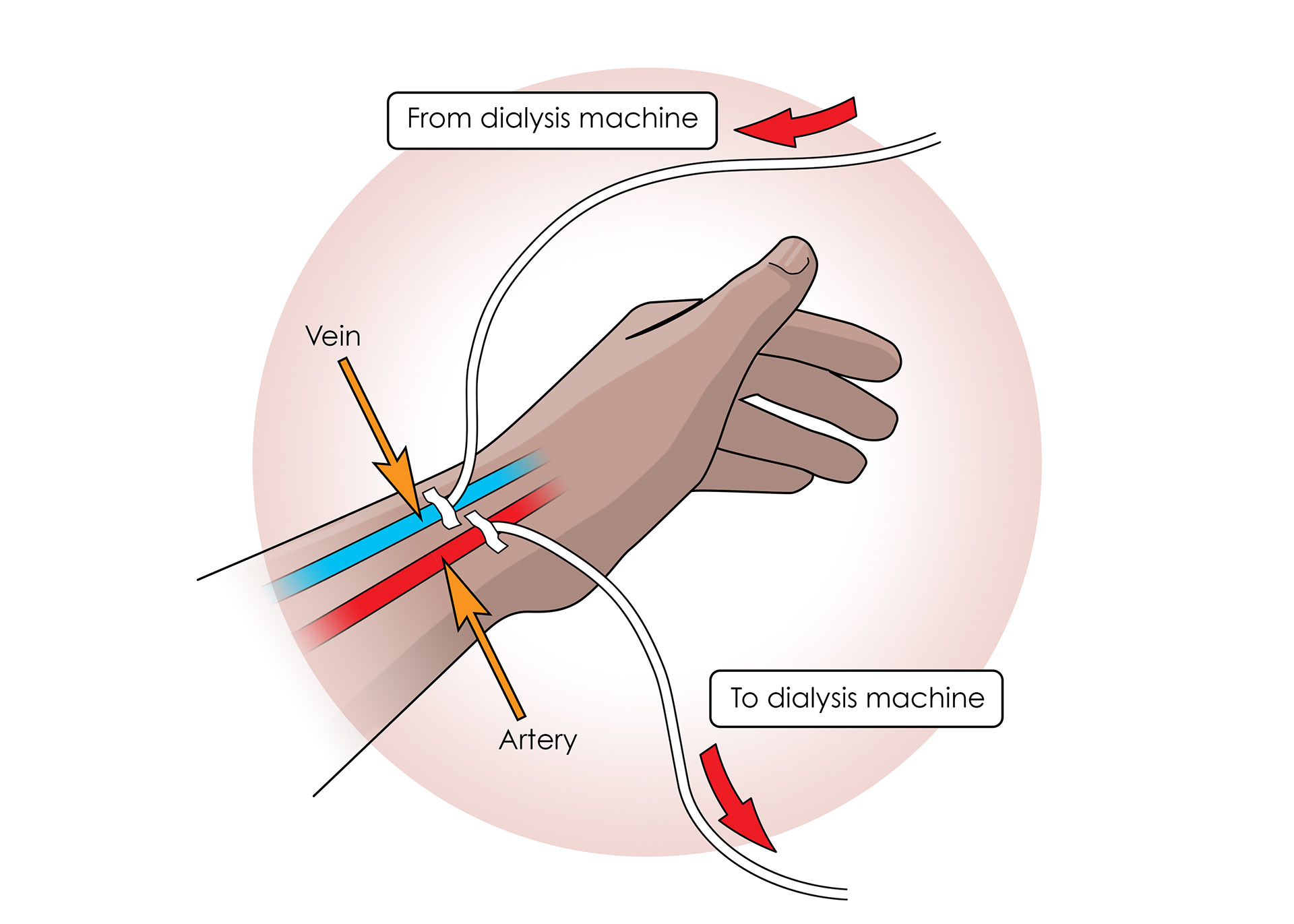
Patients are connected via arteries
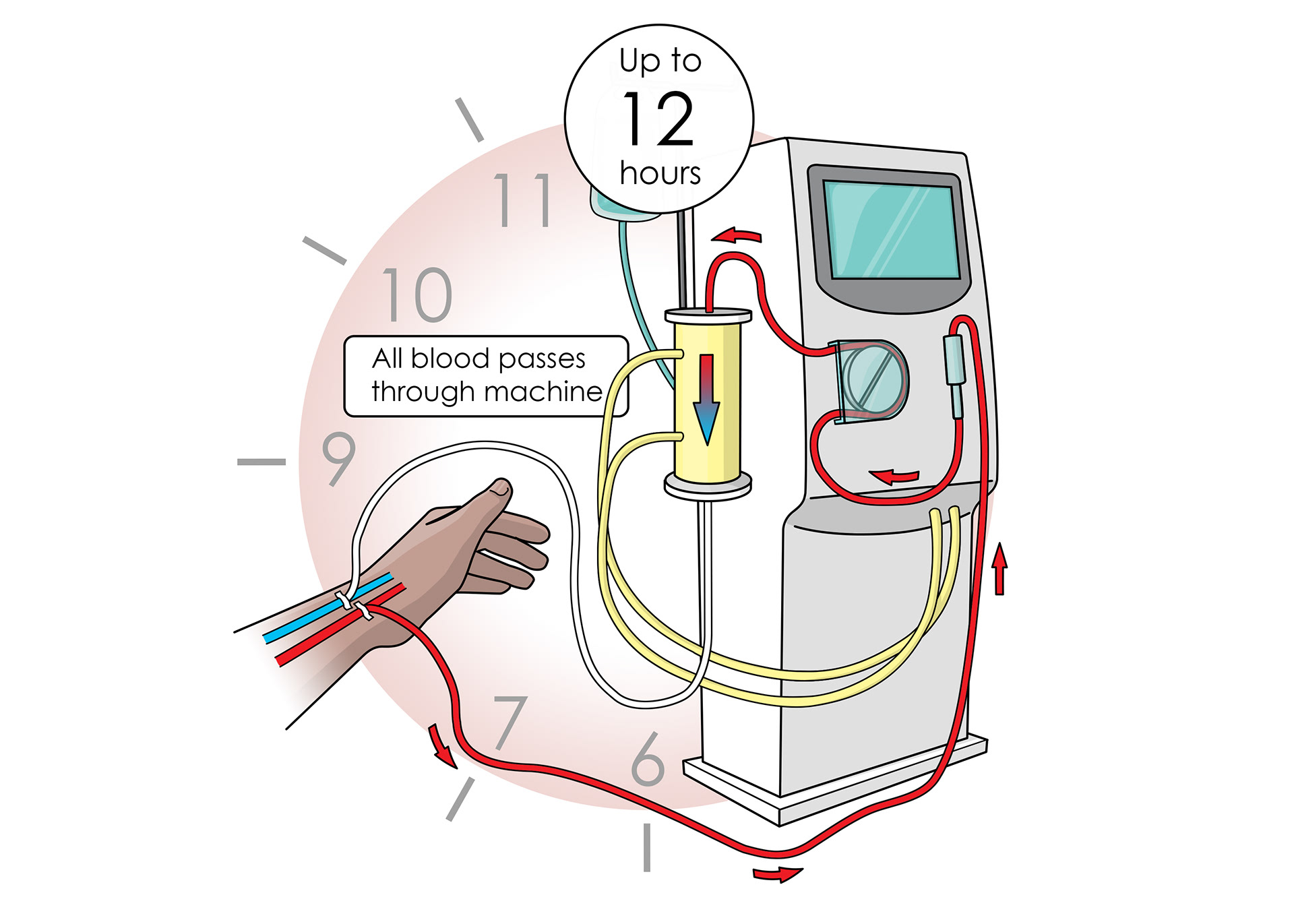
All blood passes through the machine for up to 12 hours
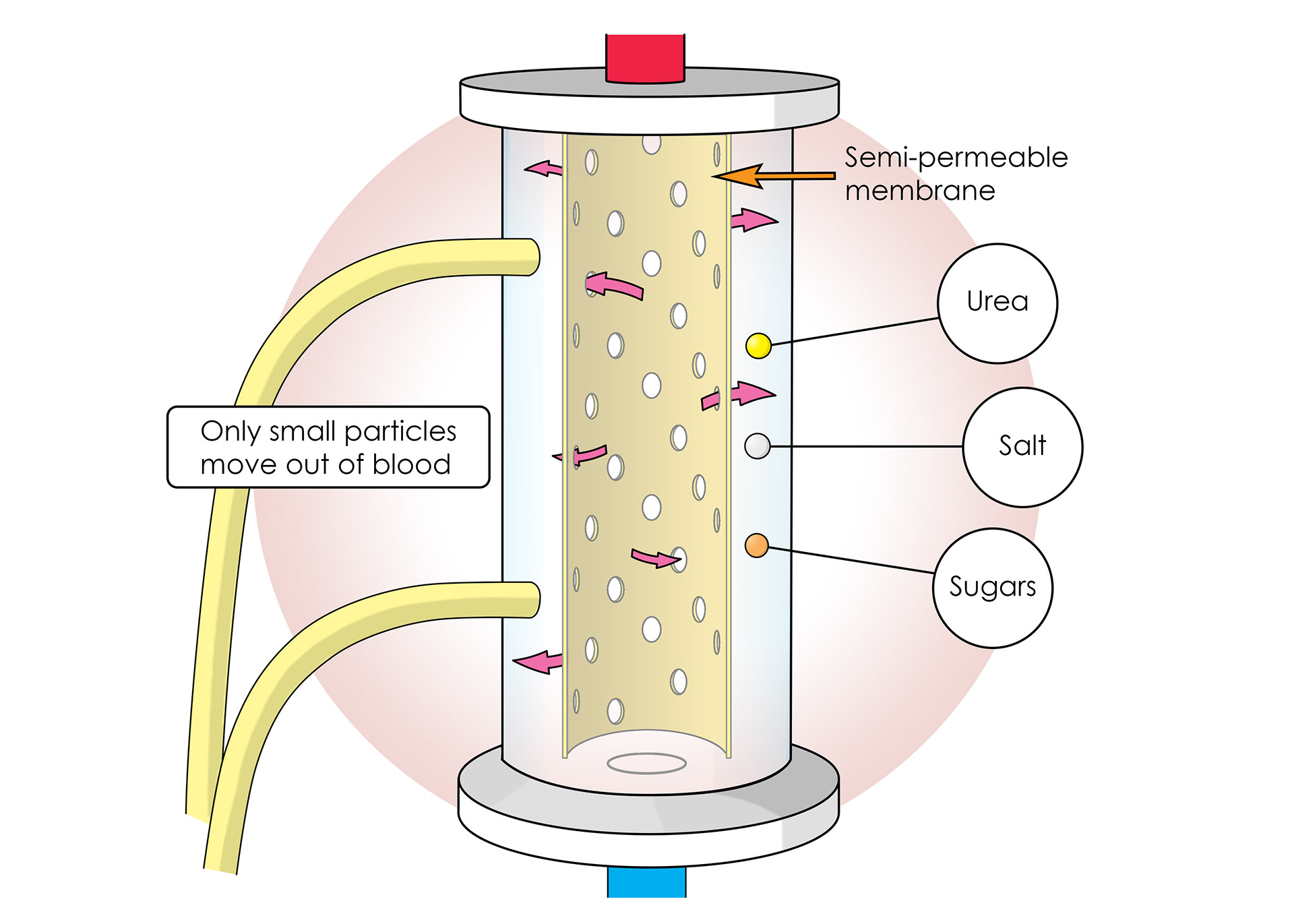
Semi-permeable membrane inside the machine only lets small particles move out of blood
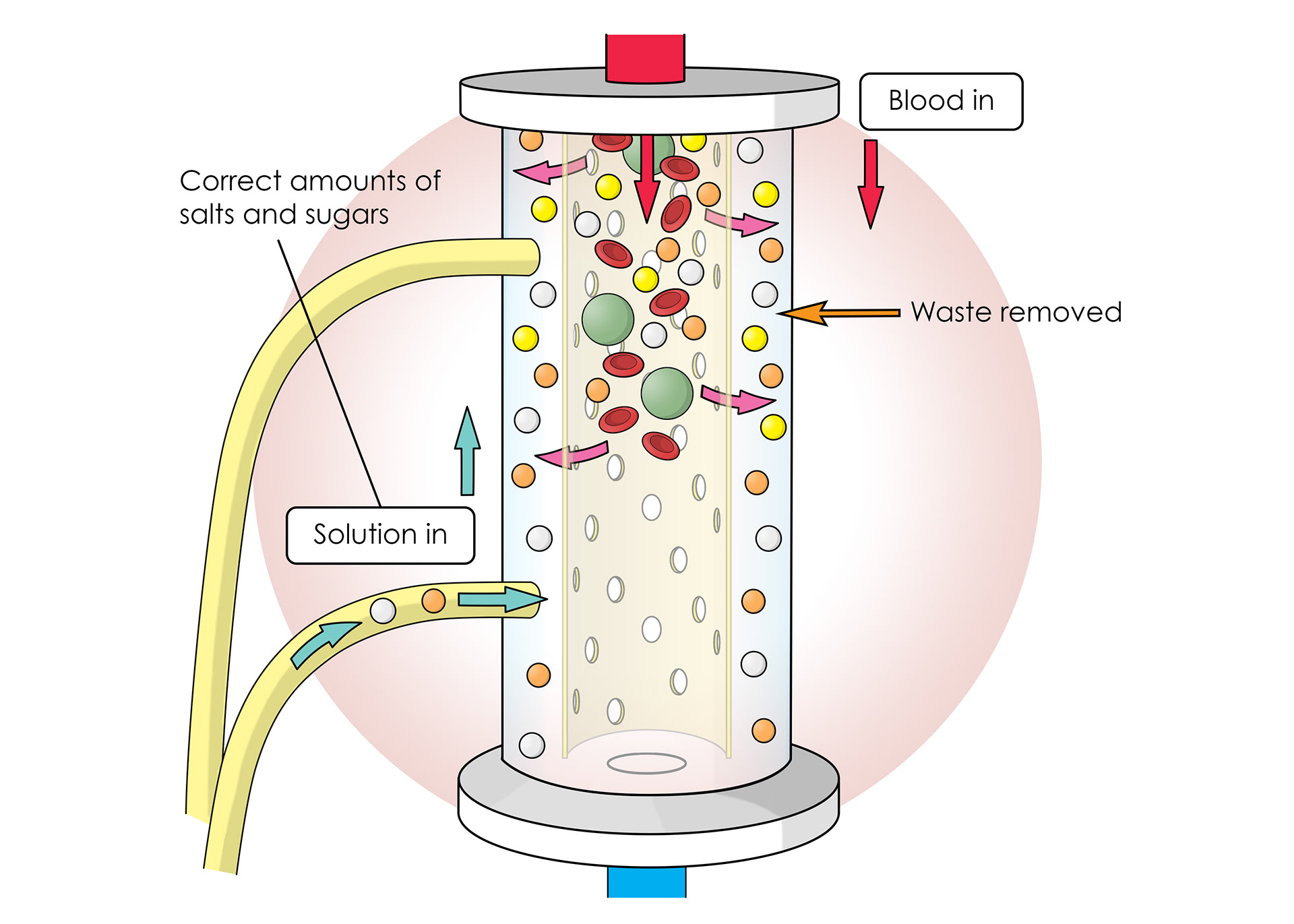
Blood passes through and waste removed
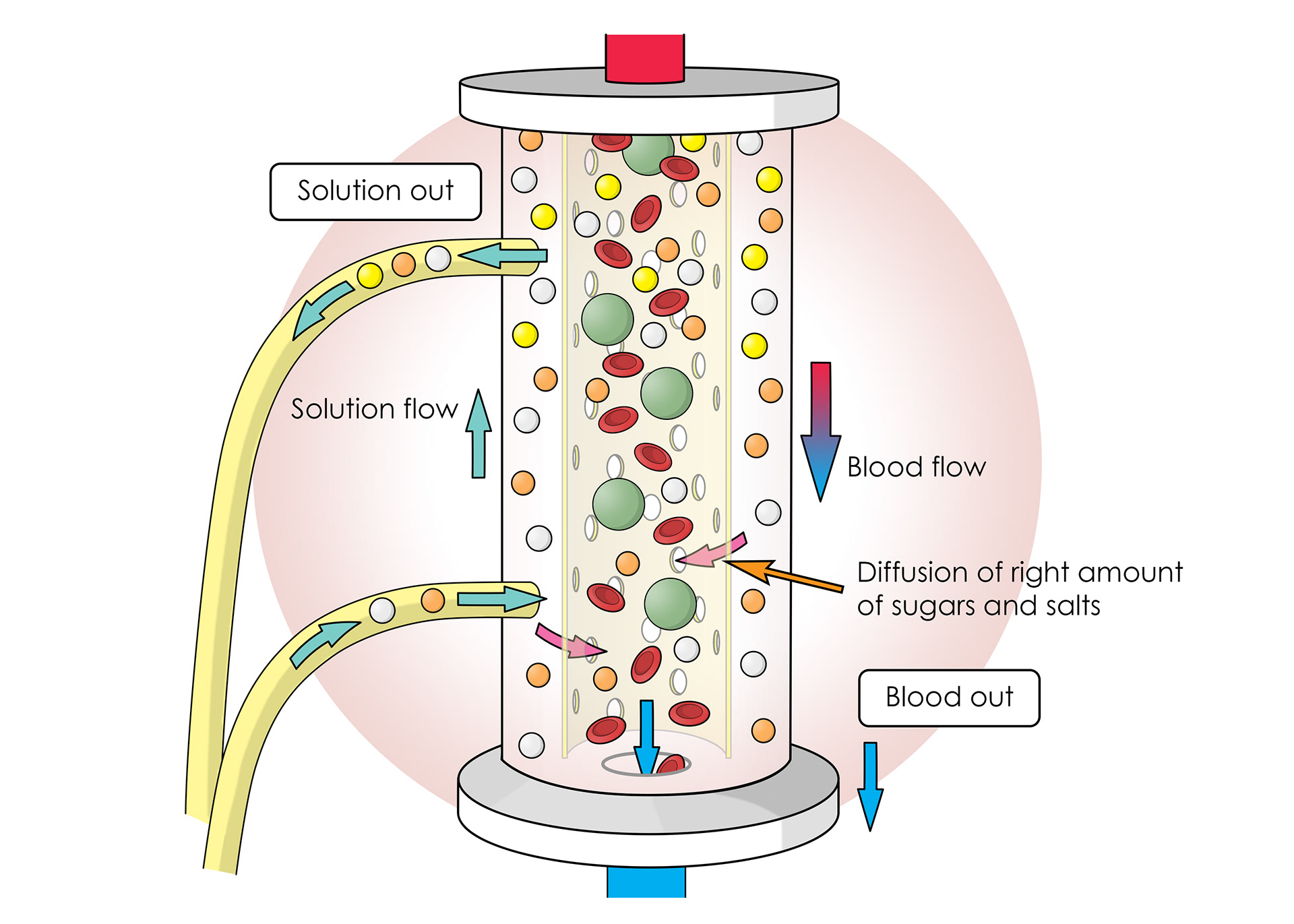
A solution provides the correct amounts of sugars and salts to move back into the blood via diffusion
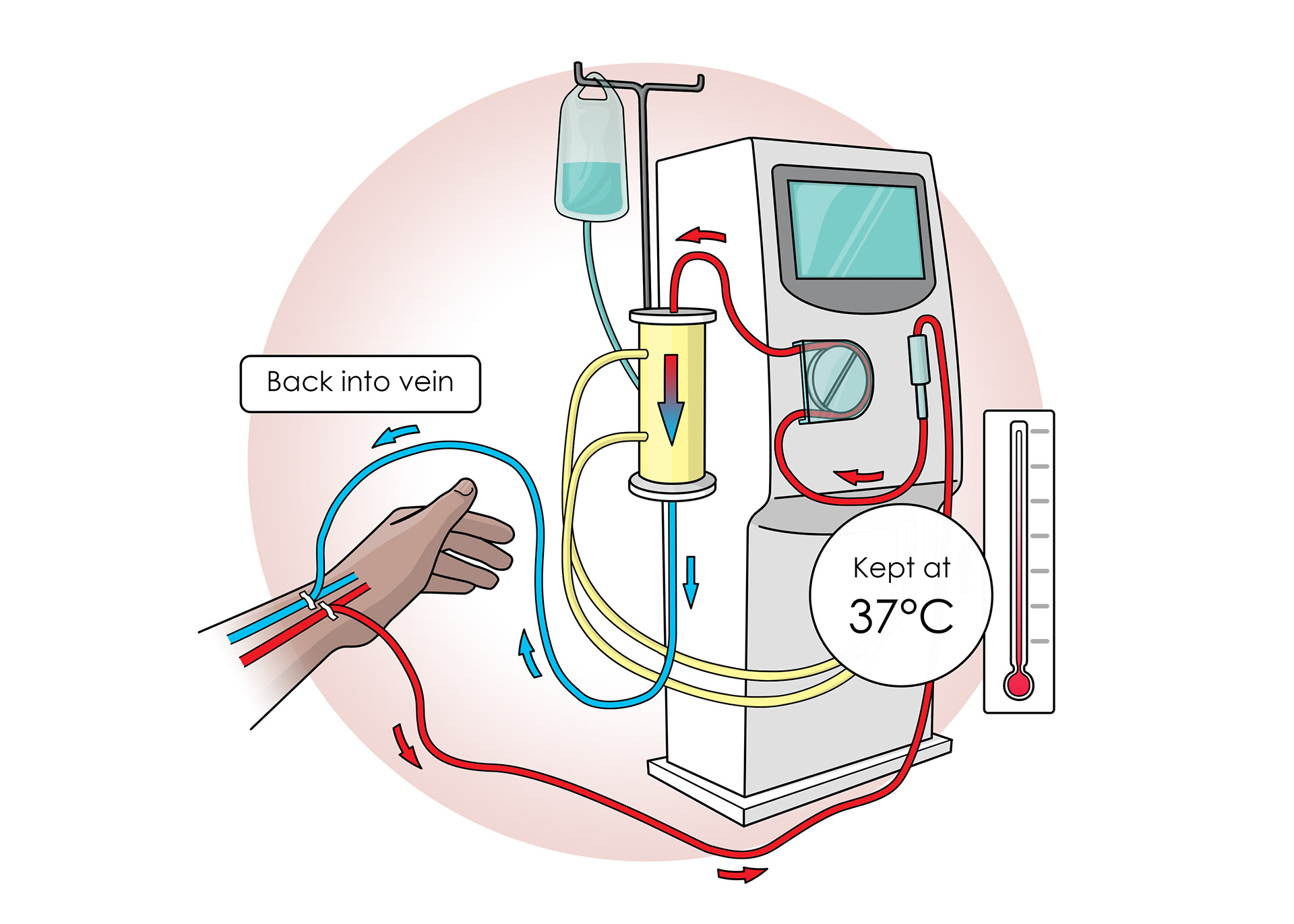
The machine keeps the blood at the correct temperature
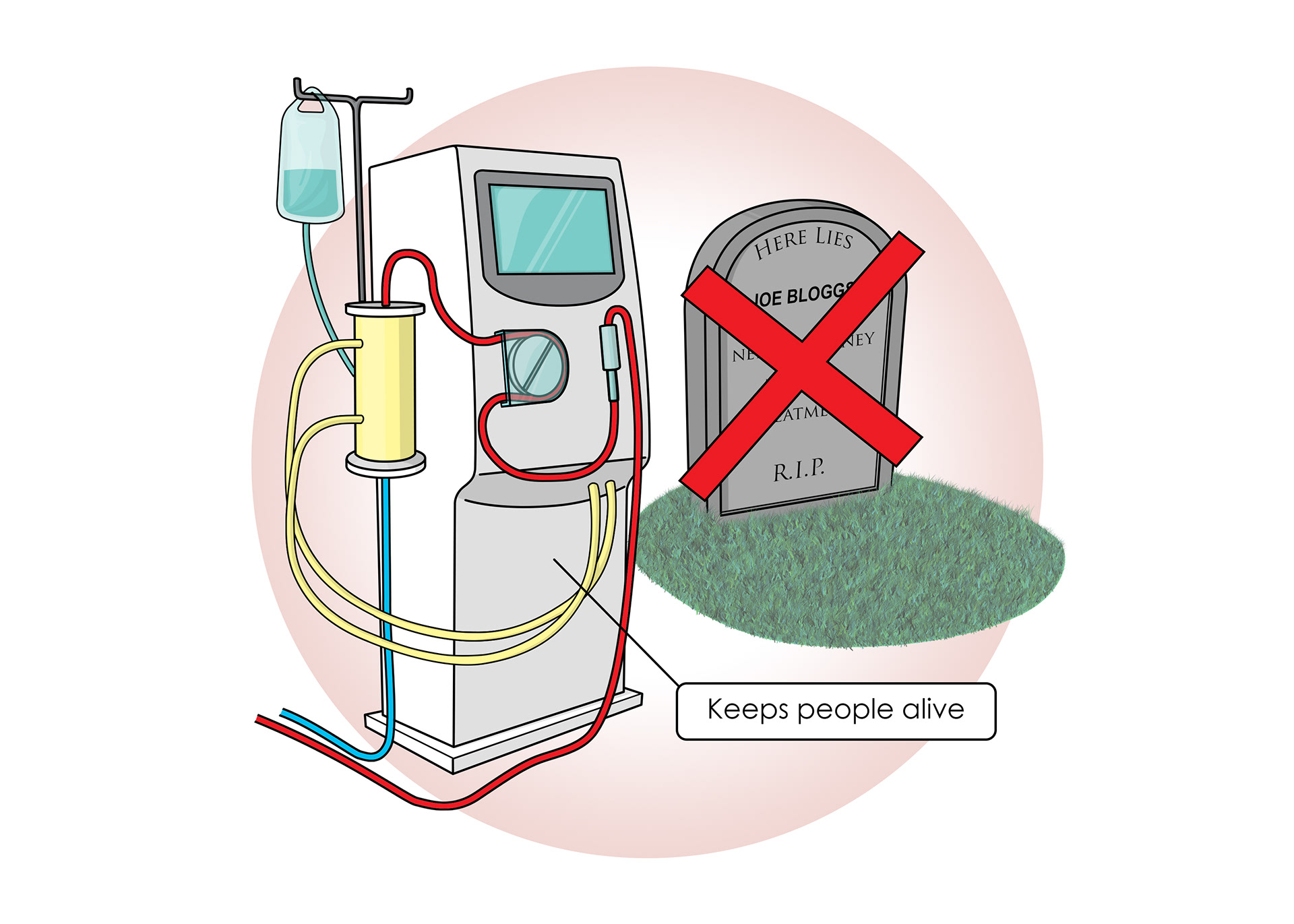
Dialysis keeps people alive
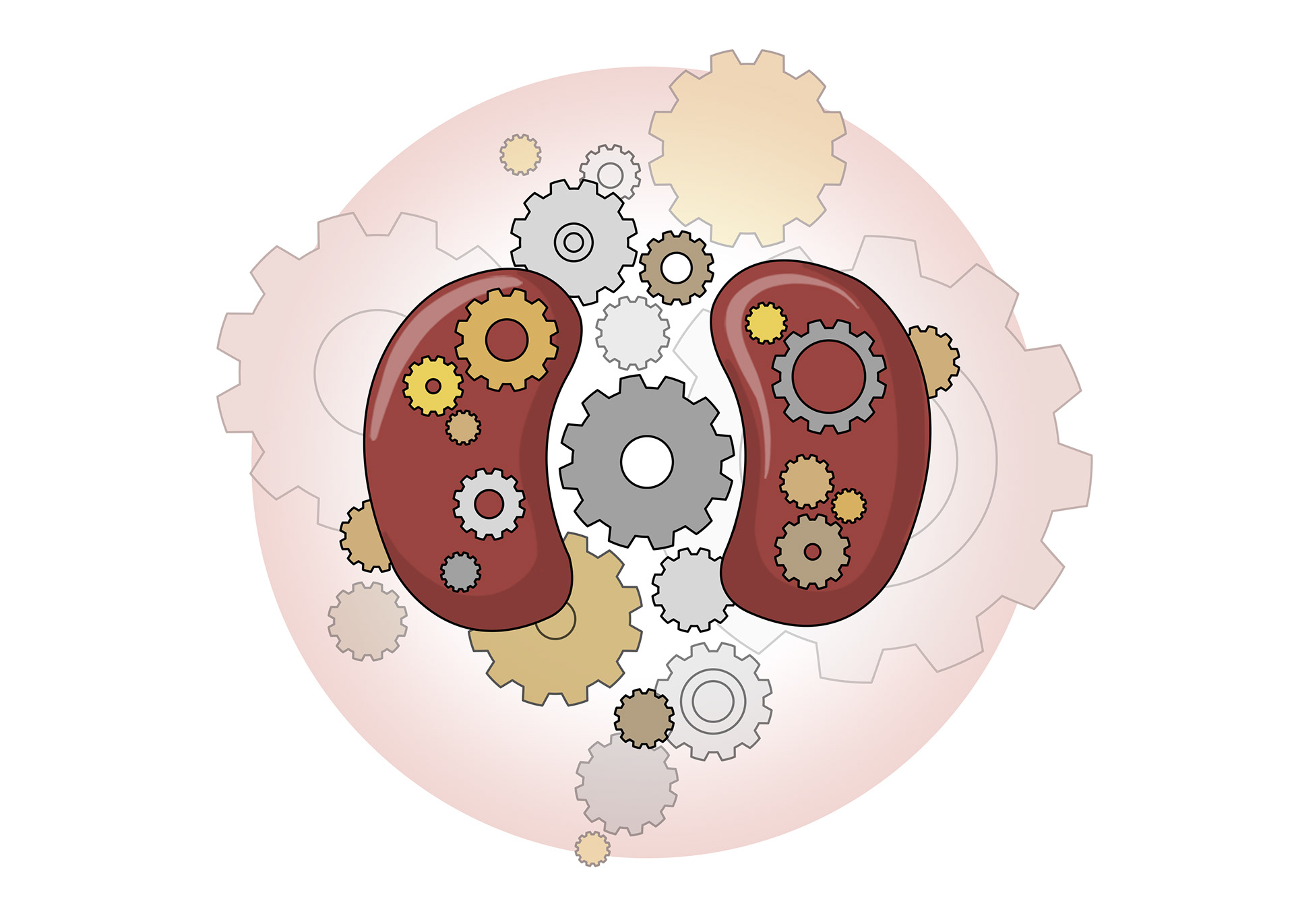
Dialysis cannot replicate all the complex functions of the kidneys
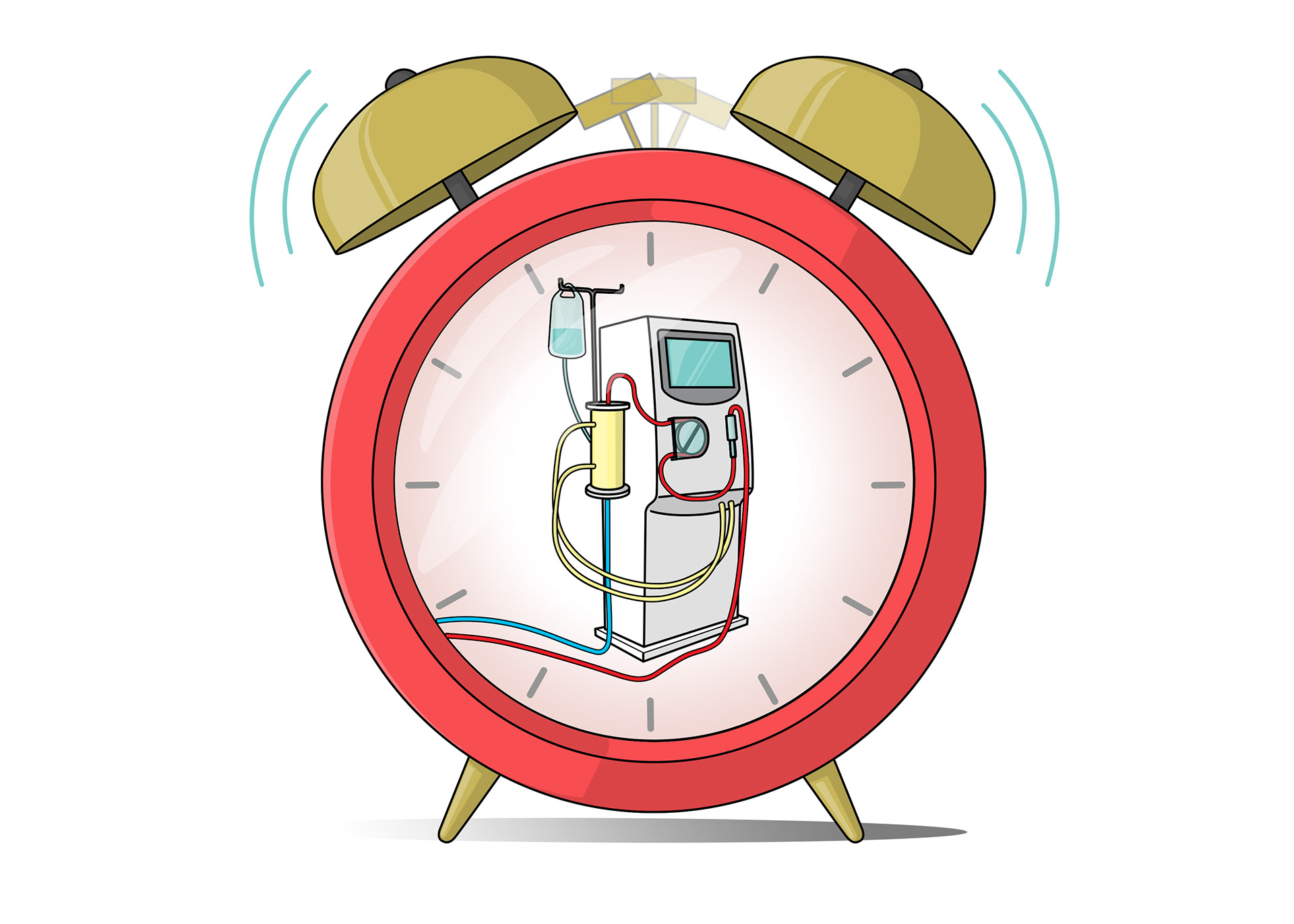
Dialysis is a short term solution only
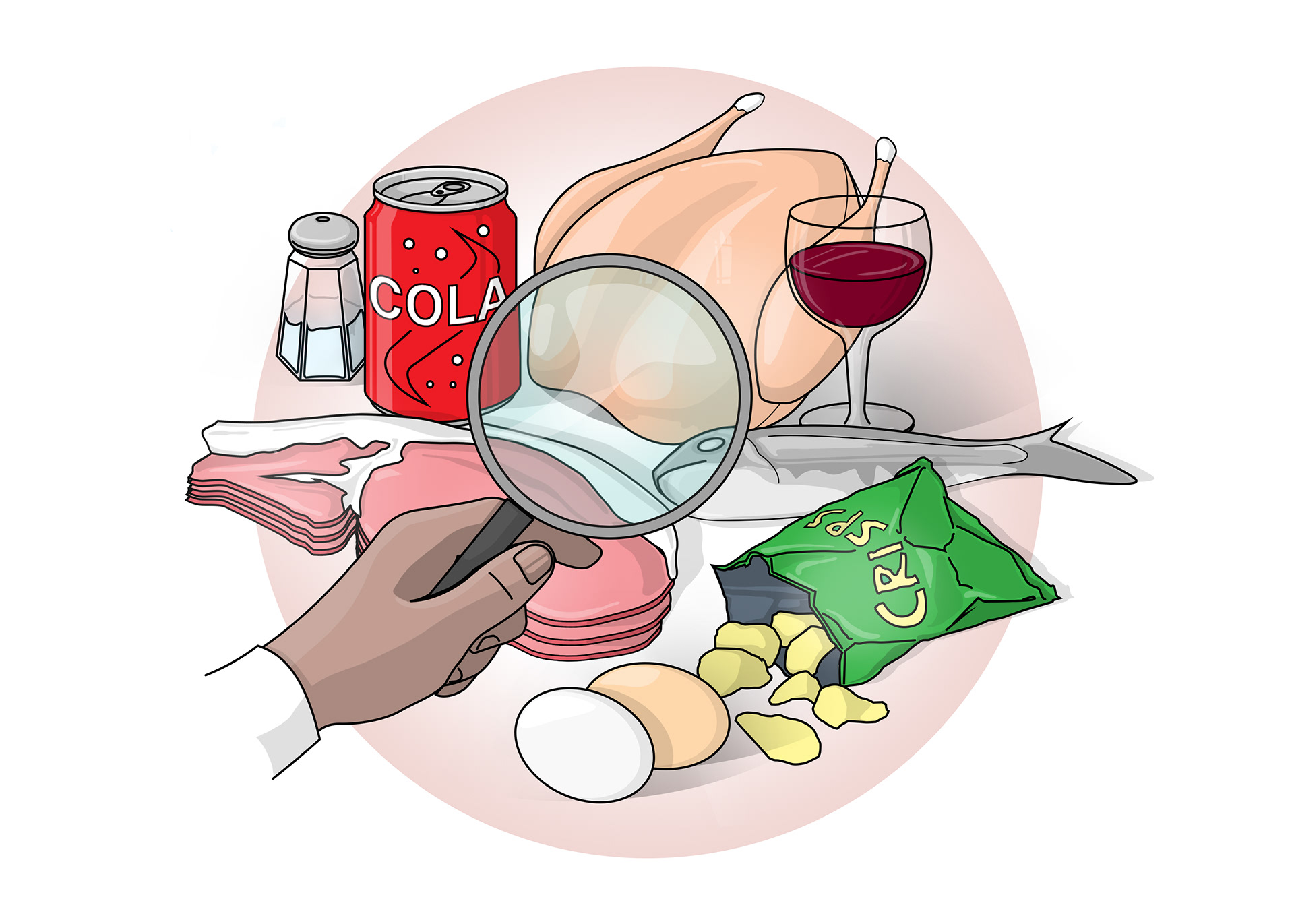
Patients must be careful of their diet
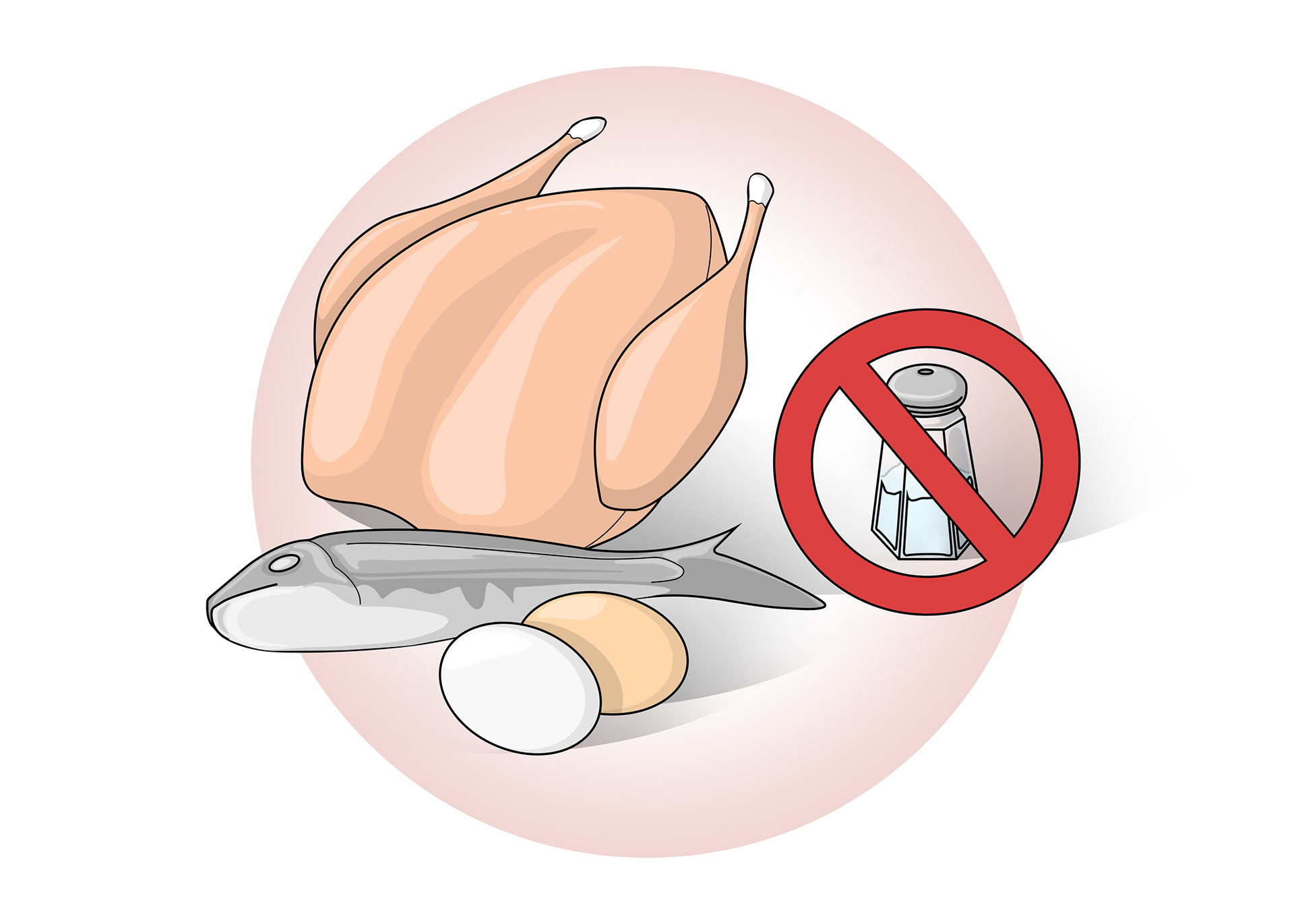
They need high protein foods and to avoid salt

Dialysis is expensive meaning that there is a waiting list
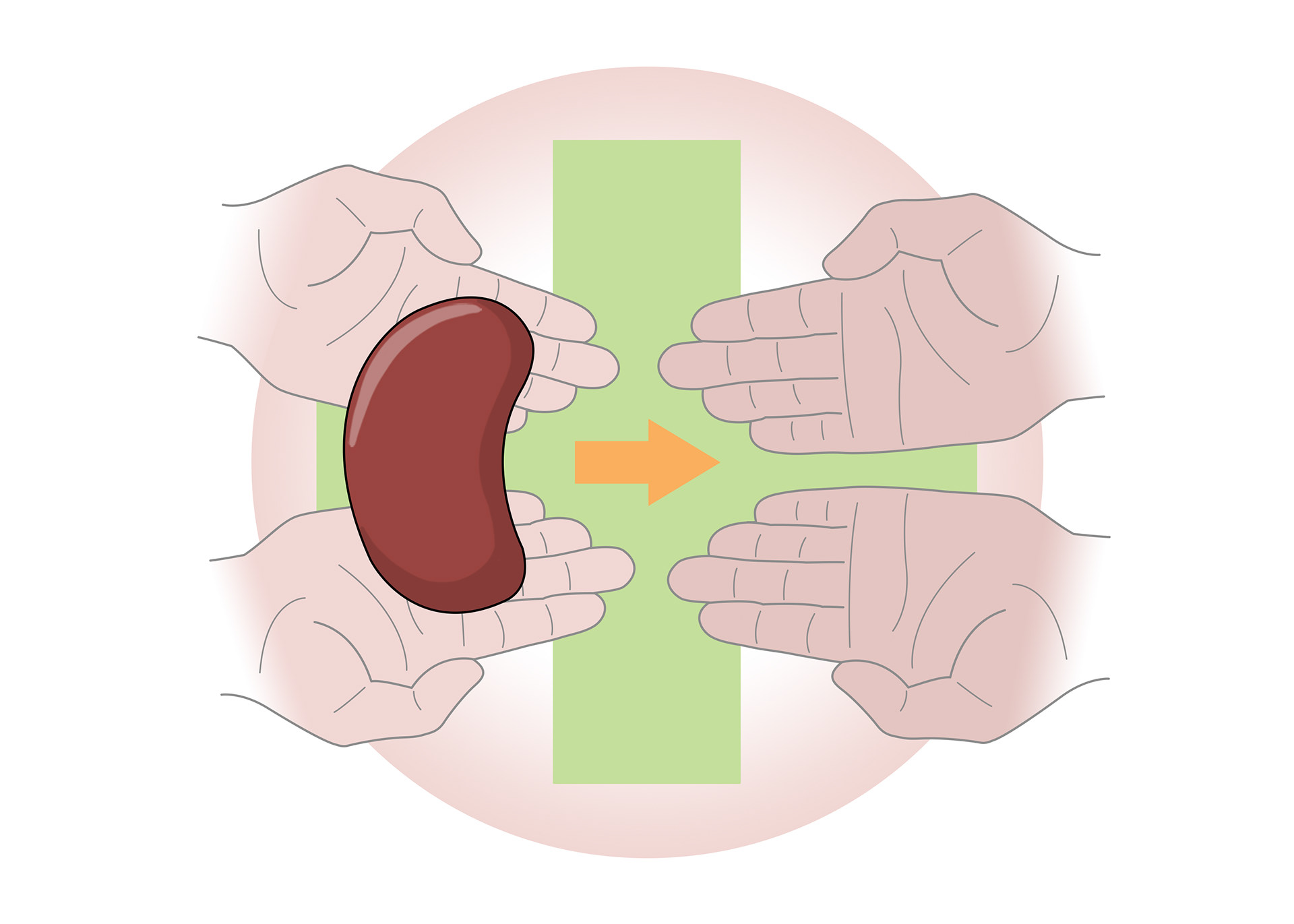
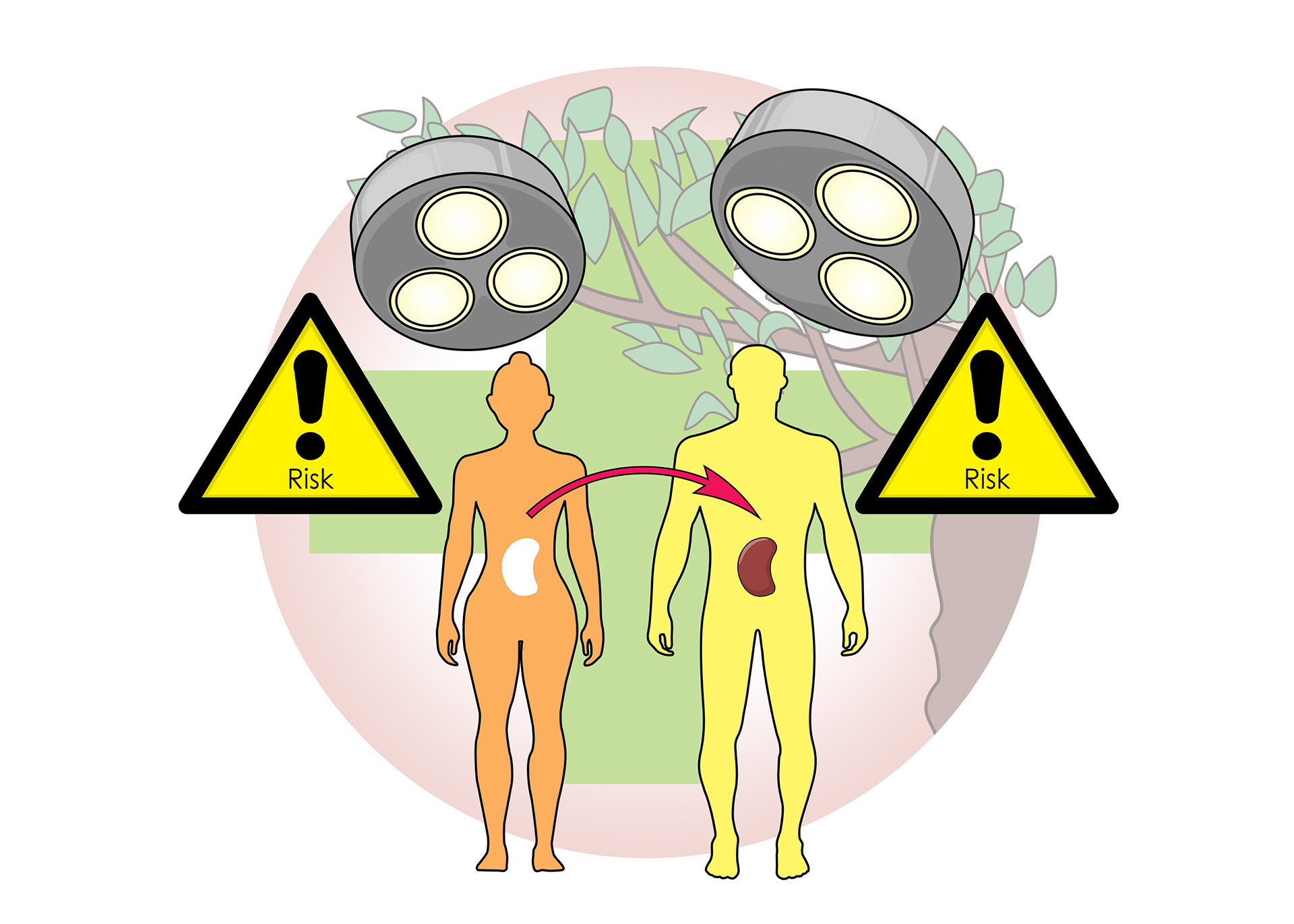
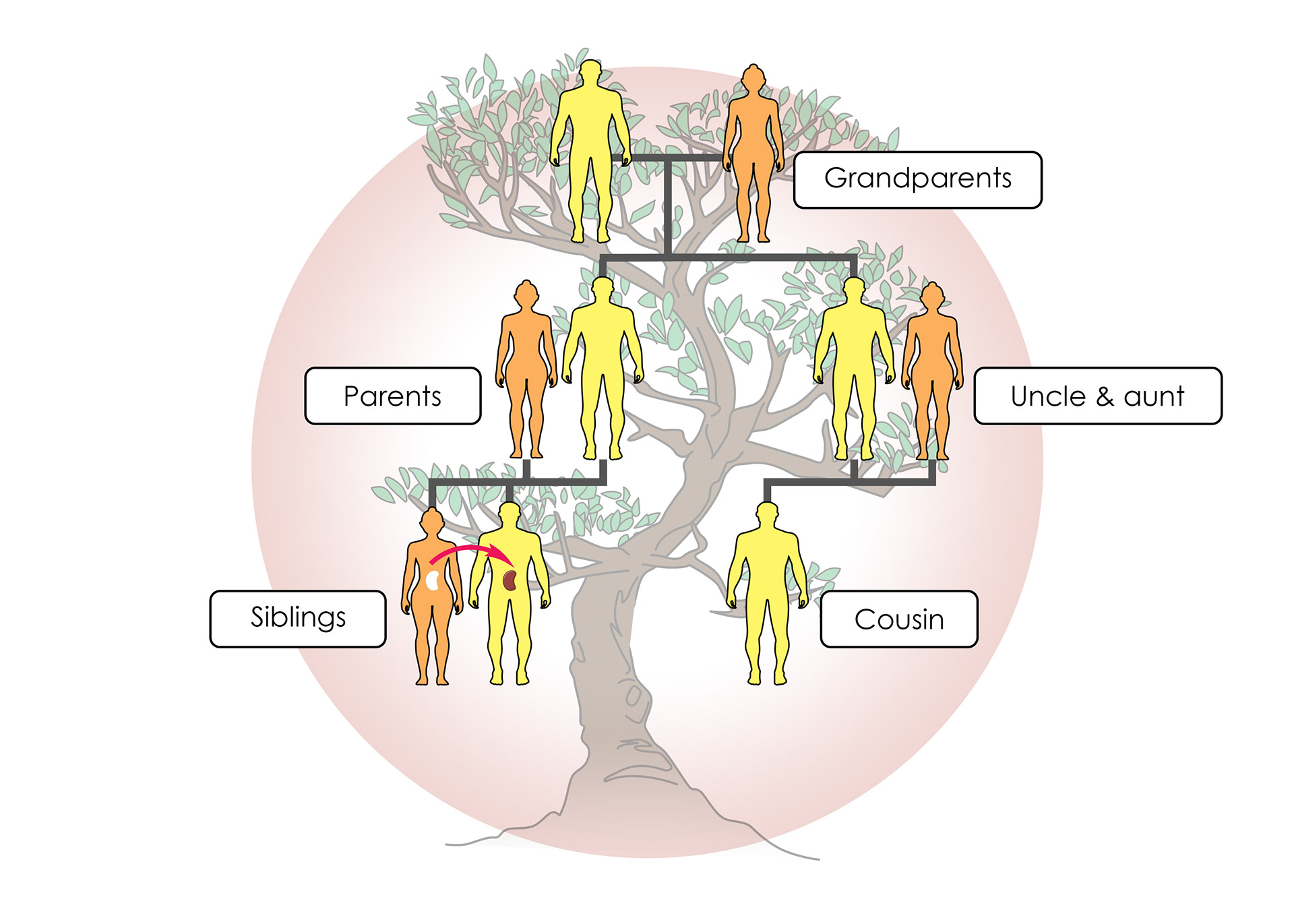
The long term treatment is kidney transplant
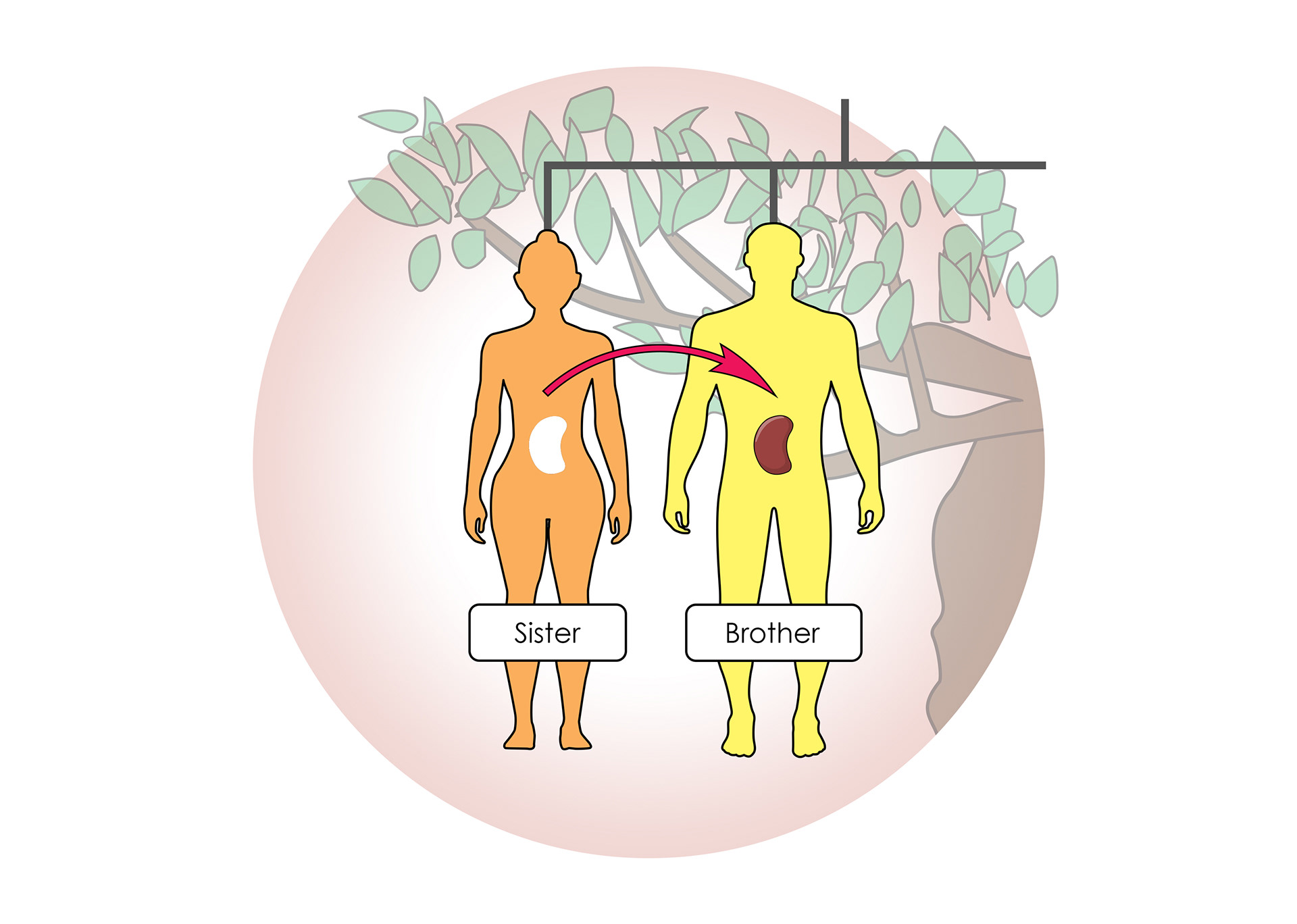
A close relative can donate a kidney
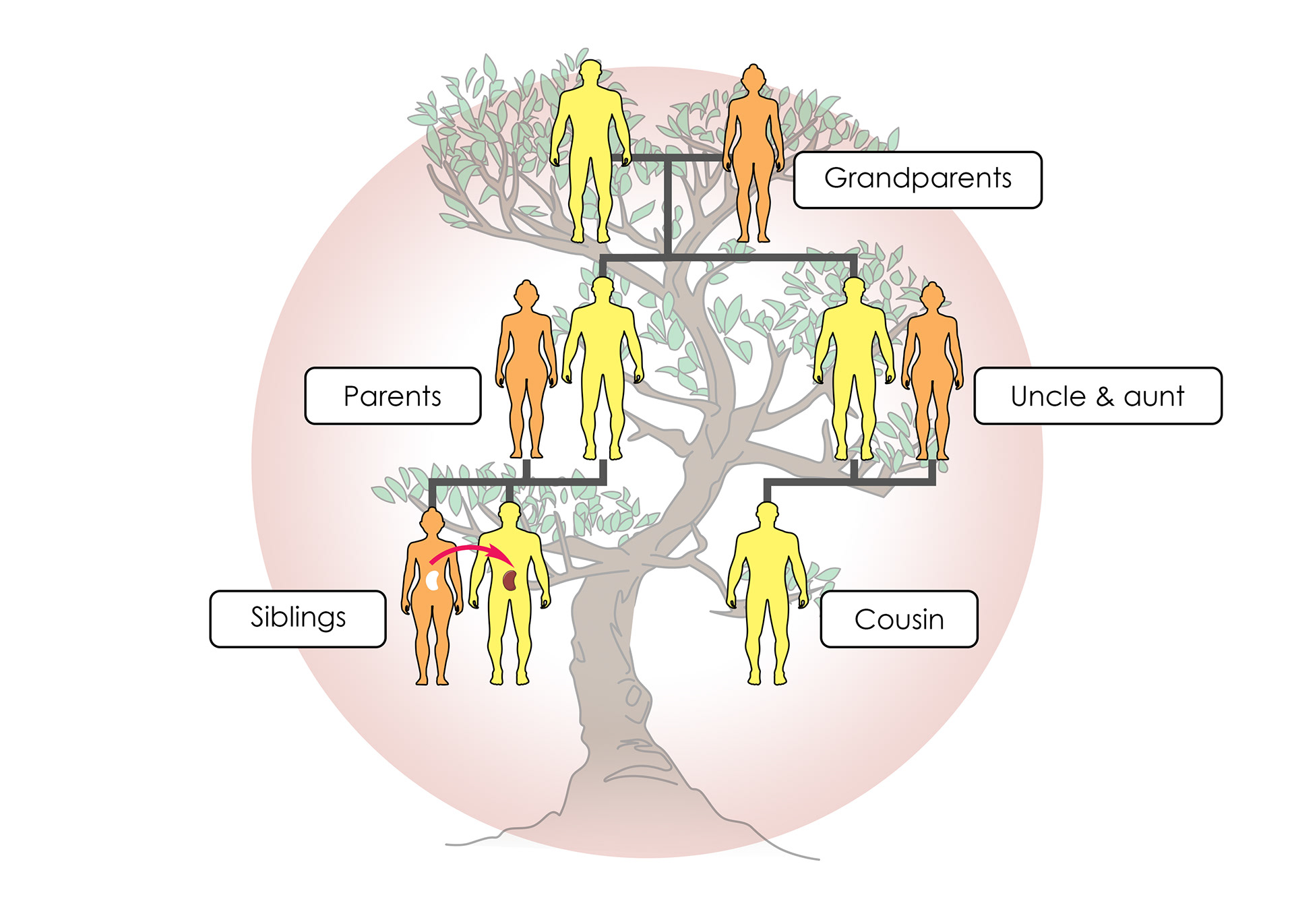
The closer the relative the less chance of the body rejecting it
Kidney transplant is major surgery